
 |
MacAPRS™
&
WinAPRS™
Documentation
|
 |

written by
Mark Sproul (KB2ICI)
and Keith Sproul (WU2Z)
The current version of MacAPRS™ is 3.8.4
The current version of WinAPRS™ is 2.8.4
Last updated Feb 28, 2006
Email the authors at kb2ici@amsat.org or
wu2z@amsat.org
Files can be downloaded from
DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY
Download the MacOSX MacAPRS for MacOS-X
Click here for info on using TIGER MAPS in WinAPRS/MacAPRS/X-APRS
What IS APRS
APRS stands for Automatic Position Reporting System.
Mac/WinAPRS is a program for utilizing mapping and GPS technology along with Ham radio (packet) for use in tracking
real time geographically related information such as the location of vehicles or the status of weather.
It has many many facets and uses.
Key Features
- Supports all standard Packet Radio TNCs
- Supports several types of map data
- Mac/WinAPRS map format
- Precision Mapping CD-ROM (Windows only)
- DEM (Digital Elevation Model) image files from USGS
- GeoTiff image files
- Standard GPS input (NMEA)
- Built in databases including zip codes and airports
- Supports all standard callbook CD-ROMs for lookup of call signs
Quick Start
- MacAPRS requires System 7 or later
- WinAPRS will run on WindowsNT, Windows95, Windows2000, and Windows XP
- Supports HF, VHF and dual mode TNCs for VHF and HF input
- Supports weather station input
- Supports GPS input
- Supports RDF (Radio Direction Finding) input
- Supports dosAPRS maps as well as the Mac/WinAPRS map format
About this document
This document is created for viewing with a Web Browser AND as printed text.
Therefore there are features of this document that may seem slightly redundant.
This way, as little is lost as possible when the document is printed.
You can download this document and view it with your web browser.
The ENTIRE documentation in web format and the images is available as a ZIP file, download it, pkunzip with -d option, then open INDEX.HTM with your favorite web browser.
This way you can have the documentation locally and not have to view it on line.
APRSdocs.zip at http://www.winaprs.org/downloads/APRSdocs.zip
Netscape has an option to add titles and page numbers to web documents when printed, this is very useful if you want to print this.
Preface
MacAPRS™ and WinAPRS™ are very similar. They are actually one set of source code, written in "C/C++" compiled for two different environments.
There are some feature differences but nothing major. Our intent is to make both versions as full featured as possible.
There are some things on the Mac that are not easily accomplished on the Windows platform that will never get implemented (such as the speech output of messages).
In this document, features found in the Mac version will be noted with the Apple Icon and features found in the Windows version will be noted by the Windows Icon.
 Mac Version
Mac Version
 Windows Version
Windows Version
Table of Contents
Overview and Setup
User Reference
Advanced Features
Troubleshooting etc
Related Documents
-
INTRODUCTION
WinAPRS™ is a version of MacAPRS™ for the Windows operating system.
WinAPRS implements the APRS™ protocol for Automatic Position Reporting System originally developed by Bob Bruninga.
MacAPRS™ and WinAPRS™ are licensed versions of APRS™. "APRS" is trademarked by Bob Bruninga, MacAPRS and WinAPRS are trademarked by Mark and Keith Sproul.
Overview
Bob Bruninga, WB4APR, developed a system for tracking objects using Packet Radio.
His system uses unconnected packets (UI frames) for transmitting the position and other information about each station or object.
He has been working on this system since 1984.
In 1992 Bob presented a paper at the ARRL Computer Networking Conference that introduced the DOS program called APRS (Automatic Position Reporting System).
APRS is a program that receives these packets and displays the objects on a map on your computer screen.
Since then, APRS has become quite popular in Packet Radio and is gaining new users daily.
MacAPRS / WinAPRS are implementations of WB4APR's APRS protocols. MacAPRS / WinAPRS are written in "C" using none of the code from Bob's original QuickBasic program.
MacAPRS / WinAPRS is designed to be fully compatible with the protocols developed by Bob Bruninga.
New Users
The APRS family of software has many uses and is many different things to different people. APRS can be used for
- Tracking moving vehicles
- Tracking yourself as you drive around
- Fox hunts
- Keeping track of weather conditions
- Watching propagation
There are many little things about APRS that users, both new and and old get caught up on, these include path settings, (WIDE, GATE, etc). The use of gateways (HF to VHF and VHF to HF).
Shareware
MacAPRS and WinAPRS are shareware. The shareware registrations are
- WinAPRS or MacAPRS $50.00
- both to the same call sign for $75.00
The downloadable versions of MacAPRS and WinAPRS are fully functional and are the SAME versions that registered users have. The only difference is that if you are not registered, you cannot save your settings. One registration covers ALL aspects, there are no hidden charges or extra charges for extra features.
When you register, you will receive a validation number. This number allows you to save your settings.
All payments MUST be in US dollars and checks must be drawn on a US bank. International money orders are also fine.
Please send shareware fees to
Mark Sproul
698 Magnolia Rd
North Brunswick, NJ 08902
Recent additions to MacAPRS and WinAPRS
Download the latest version from DOWNLOAD DIRECTORY
WinAPRS Version 2.8.4 - Feb 28, 2006
MacAPRS Version 3.8.4
- Fixed bug in Canadian Toporama display
- Many Improvements to Tiger drawing including drawing polygons from biggest to smallest
- Improved Tiger road labeling
- Added vector icons for road signs
- Fixed bug in color display of DEM (Digital Elevation Model) for Windows, added more color modes
- Added option to display Barometric presure in inches of HG
- Fixed bug in Base91 decoding thanks to Herb KB7UVC for the help
- Improvements to rotated text labels for roads
- Fixed annoying white space at right side of window when maximized
WinAPRS Version 2.8.2 - Nov 16, 2005
MacAPRS Version 3.8.2
- Fixed printing from Windows
- Fixed some callbook problems
WinAPRS Version 2.8.0 - May 10, 2005
MacAPRS Version 3.8.0
- USGS Digital Elevation Model (DEM) files now used as releif maps for TIGER map backgrounds
- ArcInfo file support (.E00)
- TIGER MAP DATA can now be automatically downloaded from within the program making Tiger maps much easier to use.
- Davis Vantage Pro weather station working
- Fixed major bug in Compressed format parsing (BASE-91)
WinAPRS Version 2.7.7 - Aug 25, 2004
MacAPRS Version 3.7.7
- Major improvements in Tiger map drawing. Specifically the first time a map was drawn
it took awhile to figure out all of the shaded areas. This has been speed up dramatically
and at the same time uses considerable less memory. HOWEVER, it takes a little longer to process
the map files into binary. It DOES NOT require the ascii files to create the new version of the
binary files.
- Back ground drawing. Much of the tiger map drawing is now done in the background. This speeds up
many of the map operations.
- Support for Toporama Canadian map images This covers 100% of Canada
- Added support for Census Bureau Gazetteer place name file. This includes searching by city.
- Added support for GPS data $GPNVP, this is a special, non standard NMEA sentance used in Korea and Japan. This was
added at the request of Korean users.
- Added TRUE rotated labels option for Tiger Map display
 System Requirements for Macintosh
System Requirements for Macintosh
MacAPRS requires System 7.0 or later.
MacAPRS will utilize multiple monitors if you have more than one monitor attached to your Mac.
 System Requirements for Windows
System Requirements for Windows
WinAPRS is written to the Win32 API fpr Womdpws95 and later.
At least Windows2000 is recommended but Windos 95 and 98 work fine.
Comm Ports 1 through 8 have been tested and all work fine.
Special note to long-time users of DOS-APRS: WinAPRS is a proper Windows application, it does NOT conform to the menu keys that were implemented under DOS-APRS. Those are a "DOS" implementation. WinAPRS follows official "Windows" programming guidelines including most of the standard control and shortcut keys.
INSTALLATION
 WinAPRS is normally distributed via the internet as a ZIP file,
To unzip the file
WinAPRS is normally distributed via the internet as a ZIP file,
To unzip the file
pkunzip -d WINAPRS.ZIP (the file name might be slightly different)
The "-d" option should make it create the necessary directories and sub-directories.
The ZIP file should unzip to exactly what is below, if it does not, follow these steps.
- Create a folder (directory) called "WinAPRS" (or what ever you want)
- Copy the following to that folder
- WinAPRS.exe
- SERDLL32.DLL
- SERTHUNK.DLL
- SER16DLL.DLL
- WINAPRS.HLP
- Either copy or create a folder called "MAPS". This folder MUST be here and must be called exactly "MAPS".
- Put any and all of your maps in the MAPS folder.
- Create a folder called "TNCfiles"
- Copy all of the TNC settings files into it
Recommended but not required
- Create a folder called DOCS (see section on Help Window)
- Copy WAPRSdoc.htm into it
Optional
- Create a folder called "DATA"
- Copy AIRPORT.DAT into this folder
- Copy ZIPCODE.DAT into this folder
- Create a folder called "LABELS"
- Copy label files into this folder (see section on global labels)
- Create a folder called "OVERLAYS"
- Copy any ".POS" files into this folder
Installation diagnostics: On startup, MacAPRS / WinAPRS checks to see if required files are present and if optional files are in the wrong place, any errors are reported. I added this after several problems from users getting things set up correctly. MacAPRS and WinAPRS are growing and expanding, the options and setup procedure are going to get more involved, I will continue to add as much intelligence into the program to assist users as I can.
Tiger Maps
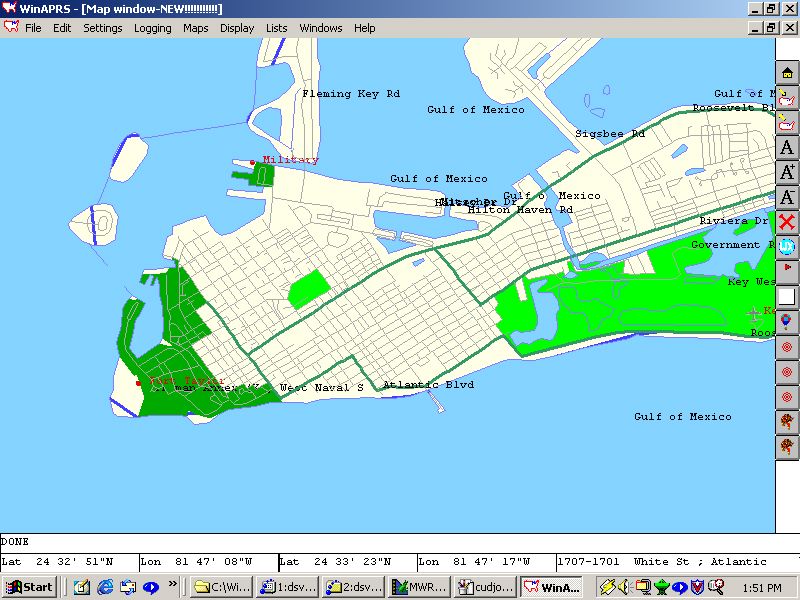
For more images click here
For samples of Puerto Rico
The US Census Bureau has mapping data for the entire USA that is the best in the world, most of the major mapping companies start
out with the data from them. This data is called TIGER Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing system
This data is very good and is updated every year. However it takes lots of memory to deal with it. Previously with WinAPRS, there has not been enough
memory or CPU power to deal with this data directly, previous versions of maps for use with WinAPRS have been derived from this data but
a lot of the information was lost when converted. Now WinAPRS/MacAPRS/X-APRS uses the data directly and you can see that the maps are
the best yet for APRS.
All of the 50 states, Washington DC, Puerto Rico, American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands,
U.S. Virgin Islands are included in this coverage
NOTE!!!
Starting with version 3.7.9/2.7.9 Mac/WinAPRS has the ability to download all of the TIGER data from within the program.
You no longer have to download manually.
You will have to unzip the zip files manully. I am working on unziping within the program but do not have it working at this time.
|
To use TIGER maps with MacAPRS/WinAPRS/X-APRS
- Create a folder inside your MacAPRS/WinAPRS/X-APRS called Tiger. On X-Windows,
it must be "Tiger" as unix is case sensitive, Mac and Windows are not.
- There are many files that can go in this directory.
- You need to download files from the US Census Bureau located at
http://www.census.gov/
- In all cases, the ASCII versions of these files are used.
- The first file to download is the US state outlines file
http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cob/st2000.html
All 50 States, D.C., and Puerto Rico - st99_d00_ascii.zip (1,800,92 bytes)
The link to the exact file is http://www.census.gov/geo/cob/bdy/st/st00ascii/st99_d00_ascii.zip
If you are running on a system with not very much ram or hard disk, you can download just the outlines of the states you want.
- If you want county outlines download them from
http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cob/co2000.html
Download them all or just the ones you want, for example, the file for New Jersey is
New Jersey - co34_d00_ascii.zip (62,328 bytes)
- For state map data, go to one of these links and click on the state (at the bottom of the page).
Download the counties that you want for your state. To look up which county
numbers are which, look at the file fipscodes.txt that should be with the
distribution files of MacAPRS/WinAPRS/X-APRS
Gazetteer
The US Census Bureau also has Gazetteer files that list names of cities. In congjunction with
the Tiger maps, The PLACES file is now supported. To make this work, download the
places2k.txt file. Save this file as is
in the "Tiger" folder.
For more information about the file, refer to
http://www.census.gov/geo/www/gazetteer/places2k.html
Toporama
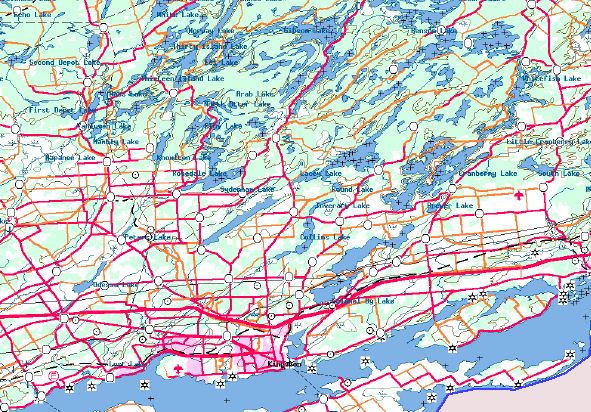
The Canadian Centre for Topographic Information has made avaialble gif images of maps of ALL of Canada.
These maps come in 2 reolutions and are very good maps. They are gif images so there is no searching or scalling.
To use the Toporama maps, create a folder called "Toporama" and places the images in that folder.
You MUST also have Tiger maps set up as these only disply in a Tiger Map window. You should download the US
state outlines at the very least.
The map images can e downloaded from
http://toporama.cits.rncan.gc.ca/
PLEASE NOTE: Due to the fact that Mac/WinAPRS uses a square mapping model, the farther north you go, the more
distored the map images appear.
CONFIGURATION

 Originally I thought that the settings for WinAPRS would have to be dramatically different from what was done for MacAPRS, this is due to the vastly different implementation of dialogs for Windows versus the MacOS. I was able to write software that read the Mac dialog resources and output Windows dialog resource descriptions. This made the conversion dramatically easier and made the dialog boxes for both versions practically identical.
Originally I thought that the settings for WinAPRS would have to be dramatically different from what was done for MacAPRS, this is due to the vastly different implementation of dialogs for Windows versus the MacOS. I was able to write software that read the Mac dialog resources and output Windows dialog resource descriptions. This made the conversion dramatically easier and made the dialog boxes for both versions practically identical.
Under the SETTINGS menu there are several different settings dialog boxes. They may not be in this order.
- Master Mode
- Normal Ham Operation - this is the default.
- Weather ONLY -- this sets all options to WEATHER mode, this is primarily for National Weather Service and SKYWARN use.
- Station - This is where you set your callsign, latitude/longitude, validation number, station type, etc.
- APRS - ID String, beacon string, time out settings
- Status Text - A status string that gets sent out periodically it can be any comment you like
- Auto track moving station - if a station is moving keep track of its movements it takes memory so some people like to turn it off
- # of points to save - if a station is being tracked, how many points to save
- Track delta - if another position comes in less than that amount of time ignore it
- Alarm delta - if the station Has alarm set, min time between alarms
- Station time out - if a station is inactive for X hours forget about it
 Serial Port - Set up comm port parameters
Serial Port - Set up comm port parameters
- TNC - TNC type, TNC init strings
- Position report settings - How often your station sends out a position report.
- Weather settings - Set your weather station type, or if you don't have one, set the current temperature, etc. manually so that you can transmit the values.
- CallBook DataBase - Set your call book CD-ROM type.
 Communications - Set up comm ports for input. This is a sub menu.
Communications - Set up comm ports for input. This is a sub menu.
 Enable Sound - Enable / Disable audio alarms
Enable Sound - Enable / Disable audio alarms
 Sound settings - set the voices for text-to-speech.
Sound settings - set the voices for text-to-speech.
 Balloon settings - Used for calculating information when tracking balloons.
Balloon settings - Used for calculating information when tracking balloons.
 GPS settings - Setting special things for GPS input
GPS settings - Setting special things for GPS input
Performance issues
MacAPRS and WinAPRS are multi-faceted programs, they have many uses for many different purposes and people.
They can utilize large amounts of system resources.
For example, if the ZIPCODE.DAT file is present in the DATA folder, it ALWAYS gets loaded into memory and kept in memory the entire time the program is running.
If the file is NOT present, then it is not loaded and the memory is not used.
If you are trying to run on smaller systems such as laptops some of these options should be removed.
Please keep this in mind when configuring your setup.
memory.txt or config.txt
Either file name can be used. It will look for config.txt first, then look for memory.txt.
Only one will be read. Since users need to be able to configure the amount of memory being allocated
for station lists etc, before the program is launched and even if they are not registered, a separate config file is set up for this purpose.
It is memory.txt. It must be located in the same directory as the WinAPRS.exe application.
It can contain the following commands. Use a single TAB to separate the command and the argument.
- STATIONS n - this tells it how many stations to allocate
- MESSAGES n - this tells it how many messages to allocate
- PKTBUFFER n - how much memory to allocate for the packet buffer (8192 minimum)
- DESTROYICONS YES/NO - this is for WinAPRS ONLY and is to help debug memory problems.
Version 2.4.0 and 2.4.1 did not destroy icons, version 2.4.2 did. This will allow users to change the setting so that we can figure out what works and what does not.
If the memory.txt file is not present, it will default to the normal station counts that it did in version 2.4.2.
startup.log
On startup, Mac/Win/X-APRS will look for a file called startup.log in the same folder as the application.
If this file is found, it will be read in and processed. This file is to have normal APRS packets in it.
These packets will be processed normally as if they just came in.
This can be used to create stations or objects that you always want to be there.
APRServe.txt
In order for Mac/Win/X-APRS to know what servers to connect to, on startup it looks for a file called APRServe.txt (case is not important for Mac/Windows but is for Unix/Linux).
This file contains the servername, port number for the various APRServers.
APRS Frequencies
APRS is used primarily on these frequencies
- VHF -144.390 MHz this is the new frequency most people are moving to
- VHF -145.790 MHz this is no longer used in most of the US
- HF - 10.151.51 Lower side band, NOTE, the carrier is actually 2125 kc down from this so it IS within the ham bands even though it doesn't seem like it.
TNC Settings
These tips may help in setting up your TNC
- Make sure HEADERLN is OFF
- Some AEA TNCs have an EXPERT mode, it must be ON
- When using DUAL MODE TNCs such as the AEA DSP-2232 and PK-900 and the KAM, there are some extra settings for switching between HF and VHF (radio 1 and radio 2).
These strings can be set in the TNC settings dialog box. If you select the correct TNC button, it will automatically set these for you.
If you are using non-standard, put your settings in the box. The defaults are
- AEA are "|0" and "|A"
- KAM are "~A" and "|A".
- If you are using a Kantronics TNC, then there are some extra settings that MUST be setup in order for Mac/WinAPRS to understand the data coming from the Kantronics TNC.
headerln off
mstamp off
cstamp off
streamev on
mresp off
mcom off
pid off
- On some AEA TNCs, BBSMSGS must be set to ON
- Dual band TNCs such as the PK-900, DSP-2232 and KAM PLUS need to be used on the HF (Dual) port and not on the VHF port. This is true even if you are using VHF only.
Pico Packet setup with GPS input
The Paccomm PicoPacket TNC has the advantage of having a second serial port input that can be connected to a GPS.
This solves the problem of needing 2 serial ports on a laptop.
Operation:
The GPSTEXT parameter specifies the NEMA string that is to be parsed. The
parsed string is placed in the LTEXT buffer. When the PicoPacket receives
a Control-E the contents of the LTEXT buffer is sent to the computer.The
check boxes in the "GPS Settings..." specifies which computer port the
string is to be sent. With the above settings, WinAPRS will automatically
send a Control-E to the PicoPacket in approximately one minute intervals.
To use the PicoPacket TNC with WinAPRS and a GPS attached to the TNC, configure as follows.
- Under "SETTINGS" menu: Select "TNC Settings...."
Make sure the following commands are in the TNC Command strings
- GPSTEXT $GPGGA
- LGETchar $05
- GPS OFF
- Under Settings menu, select Serial Port Settings
For the port in question (VHF or HF), click ENABLE PICO (^E)
- Mac version: Select "GPS Settings..."
Check either "Accept GPS data on HF TNC Port" or "Accept GPS data on VHF TNC Port" depending on band being used. If GPS ICON on the map is desired also check "Display ICON on GPS Data"
The following TNCs have been thoroughly tested with MacAPRS and WinAPRS
- AEA PK-232
- AEA DSP-2232
- AEA PK-900
- PacComm Tiny 2
- Kantronics KPC
Additional TNC settings STARTUP and SHUTDOWN
MacAPRS / WinAPRS will additionally transmit a text file to the TNC on startup and shutdown.
These files can contain any TNC commands that you may need and may be of any length.
Lines starting with "*" or "!" are comments and not passed to the TNC.
Since you can have more than one TNC in use, Mac/WinAPRS looks for several file names, the first one it finds in each catogory is the one used.
Once it finds one of them, it does not look for any of the remaining names.
These are determined at STARTUP of the program, to see which file is currently being used, refer to the Internal State Window.
The files used for dosAPRS will work just fine for WinAPRS and MacAPRS.
- VHF Port Startup
- InitVHF.TNC
- INITTAPR.TNC
- INITAEA.TNC
- HF (Dual) Port Startup
- InitHF.TNC
- INITTAPR.TNC
- INITAEA.TNC
- VHF Port Shutdown
- ExitVHF.TNC
- RESTORE.TNC
- HF (Dual) Port Shutdown
- ExitHF.TNC
- RESTORE.TNC
TNC Selection
Under the SETTINGS Menu is "TNC Selection", this displays a list of all of the TNC setup files in the directory "TNCfiles", these files are supplied as standard TNC setup files as described above for each of several different brand and model of TNCs.
Select the mode and TNC model that you will be using.
Please note: the settings contained in each of these TNC files may not be perfect for your station but are an attempt to make initial setup easier and quicker.
TNC Commands Menu
Under the SETTINGS menu, there is a sub menu called TNC COMMANDS, under this there are several commands to send APRS strings and affect the TNC.
KISS Mode
KISS mode is where the computer does all of the AX25 formatting instead of the TNC.
This takes a fair amount more work on the computer's part but facilitates a lot of advanced options.
For example, if running in normal TNC mode, to change the path, the software has to tell the TNC to first EXIT CONVerse mode, issue \
the change proto command UNPROTO APRS via NEW,PATH, then issue CONVerse again.
Under KISS mode, the path is all controlled by the software since it actuatlly does the formatting of packet.
Also KISS mode gets rid of any problems with TNC settings, everything is done in the software.
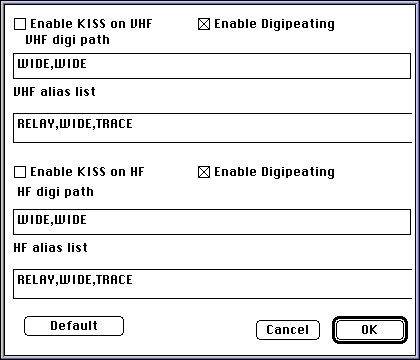
Kiss mode settings dialog box
The advantages of KISS mode
First, under KISS mode, the TNC settings such as HEADERLN, PACLEN, aliases, etc. etc. are no longer needed. Everything is handled inside of the program.
Second and most important, is unproto path, to change the path in normal mode TNC, you have to send a control-C, then wait, then send the path "UNPROTO xxx VIA yyy,zzz", the send CONV, then send the new packet, then do this all over again to set it back.
All of this and you are NOT guaranteed that the packet will go out with the new path.
If the channel was busy and the packet did not get out.
It will go out with the path that is set at the time of transmission out the RADIO, not the path that was set when the packet was sent from the computer to the TNC.
Under KISS mode, EVERY packet can have its own path, in some areas, this can be very important.
I am working on message REVERSE PATH, whereby, when you REPLY to a message, the reverse path is used to send the message back to the station that sent it.
For example, if a message gets to you via X,Y,Z, then the most probable path to get a message back is via Z,Y,X.
This hopefully will increase the reliability of getting messages through and at the same time reduce wasted packets.
AGWPE / Baycom / Soundblaster support
AGWPE is the AGW Packet Engine written by SV2AGW.
This software is a standalone packet engine that basically does nothing but talk to TNCs.
It gives other program a uniform interface to talk to any TNC, be it a normal TNC-2 design or a Baycom or a soundblaster hooked up to a radio.
Refer to http://www.raag.org/sv2agw/index.html for full information.
The AGWPE packet engine allows multiple programs to talk to the TNC at the same time.
This means you can run WinAPRS and a BBS program and a DX cluster all at the same time with one TNC. (they have to be on the same frequency).
Additionally, the TNC can be on a separate computer.
The ability to run on a SEPARATE computer is VERY IMPORTANT This allows MacAPRS and X-APRS users to use this feature as well if they have a Windows Box available.
Other advantages include
- Connecting to a TNC in some other location, i.e. the one at home from work.
- Multiple machines utilizing the same TNC at the same time.
Installation of AGWPE
- Even though the docs of AGWPE say that it will run under Windows95, I have not found the TCP connection to be reliable, therefore I recommend Windows98.
- For Win98, there is no real installation required, just copy the software.
- Double click on the AGWPE.EXE icon. Not much happens, but an entry will show up on the task bar.
- RIGHT CLICK on this button, a pop-up menu will display, select PROPERTIES. Then, click NEW PORT and configure the TNC port accordingly.
Once AGWPE is configured, in WinAPRS go to SETTINGS / PORTS.
This will bring up a list, It should be pre-configured with an entry for AGWPE on LOCAL.
Select this entry and click the OPEN button. That is all there is to it.
If you want to run AGWPE on a separate machine, go to your WinAPRS/MacAPRS directory, and find the PORTS folder.
The latest version should create that folder for you.
Inside it will be files. Duplicate the AGWPE.PRT file and edit it to contain the TCP/IP address of the machine you are running AGWPE on.
Then proceed as above.
The AGWPE program is shareware, however, he only requires registration if you are using the TCP over AX-25 option.
Port Objects
Starting with WinAPRS version 2.4.0 there is a new way to specify ports.
This is called port objects. This will be the only way to deal with ports in X-APRS and eventually MacAPRS and WinAPRS will switch entirely to this new methodology.
This method will allow as many TNCs, Weather stations, etc. as you want to have installed.
The definitions for these port objects is kept in a folder called PORTS.
The files are simple ASCII text files with parameters for configuring the port.
If the PORTS folder is missing, it will get created automatically with some default definitions.
If you are upgrading from version 2.4.0 or later to a newer version.
Then the simplest way to figure out any new settings is to rename the PORTS folder to PORTS_OLD and let it create the ports forlder anew.
Then look at the sample files for changes.
It is important to understand, not all keywords are used for all types of ports.
For example, the AGWTNC number is meaningless for a normal TCP connection.
If these are not needed, they will be simply ignored.
Eventually there will be a dialog box to allow editing/creating these definitions.
Port Objects Keywords
(sorted alphabetically)
|
| Keyword |
argument |
default |
comment |
| AGWTNC |
number |
0 |
AGWPE can define multiple TNCs to be used simultaneously. I |
| BAND |
string |
VHF |
UHF, VHF, HF, TCP
This will be used to indicate elsewhere in APRS as to where the data came from |
| BAUD |
number |
9600 |
Baud rate, only applies to type SERIAL |
| COMPORT |
string |
COM1 |
for serial devies it is the port, i.e. COM1 |
| HOST |
string |
127.0.0.1 |
hostname:port - i.e 127.0.0.1:8000 is the LOCAL address for AGWPE |
| NAME |
string |
no-name |
User assigned name for port (31 chars max) |
| PARSER |
string |
APRS |
"APRS", "AGWPE" are the only options for now, more will come |
| PATH |
string |
WIDE,WIDE |
the default path for this port |
| STOPBITS |
number |
1 |
For serial port |
| TCPPORT |
number |
10151 |
Not needed if the port is specified with the host address.
Whichever comes LAST in the file will be used |
| TYPE |
string |
none |
"SERIAL" or "TCP" as of Version 2.4.1, only TCP is implemented |
Help Window
At any time in the program you can press the F-1 key and get the help window.
This is in addition to the WinHelp functionality.
This help window is different in that it will take you to different parts of the documentation depending on which window you have in the foreground.
The help file is the WAPRSdoc.htm HTML document. Built in is a simple HTML parser.
The help file is not loaded until the first time you access it, then it is kept in memory.
The WAPRSdoc.htm file must be in a directory called "Docs" which must be in the same directory as WinAPRS.EXE
MAPS

 The map file format for WinAPRS is EXACTLY the same as MacAPRS.
This means that all of the maps developed for MacAPRS are usable for WinAPRS.
You must have a "Maps" folder (directory) in the same folder as the MacAPRS / WinAPRS application.
All Maps must be placed inside this folder.
You can have folders inside of the map folder.
These will be displayed as hierarchical menus.
The map file format for WinAPRS is EXACTLY the same as MacAPRS.
This means that all of the maps developed for MacAPRS are usable for WinAPRS.
You must have a "Maps" folder (directory) in the same folder as the MacAPRS / WinAPRS application.
All Maps must be placed inside this folder.
You can have folders inside of the map folder.
These will be displayed as hierarchical menus.
The maps that are used with DOS-APRS work just as well, simply put them into the same MAPS folder and they will show up in the MAP menu.
There is no "MAPLIST.DAT" file as there is in DOS-APRS. All you have to do is put the maps in the MAPS directory and run the program.
Please note that the DOS-APRS maps have far less resolution than the MacAPRS maps.
They have a maximum of 3000 points. We have some MacAPRS maps that have 130,000 points and recently created one map that has 250,000 points (it took a few seconds to draw).
On Windows, if you put too many maps in the Maps folder, you can't see all of them in the menu.
Go to the Map List window. You can double click on the map there and it will bring up a new window with that map.
Maps from the CD-ROM we produced must be copied from the CD-ROM to the MAPS directory before they can be used with WinAPRS.
Please note that if you put maps in the folder while MacAPRS / WinAPRS is running, you have to quit and restart before it will recognize the new maps.
NOTE: The ability to directly read DOS-APRS maps is new for MacAPRS as of Version 2.2.0.
You can hold down the option key (Mac) then click and drag the mouse, the area selected will become the new map zoom area.
For Windows, use the right mouse button.
The format for the map file is explained in a separate document, please refer to Map File Format Documentation
 Some of the maps for Macintosh on the TAPR FTP site are in Macintosh "sit.hqx" format.
This is similar to ZIP format for PCs, but of course not compatible.
We have found a PC program called SITEX10.EXE that allows decompression of these files on PCs.
It can be found at:
Some of the maps for Macintosh on the TAPR FTP site are in Macintosh "sit.hqx" format.
This is similar to ZIP format for PCs, but of course not compatible.
We have found a PC program called SITEX10.EXE that allows decompression of these files on PCs.
It can be found at:
Mac/WinAPRS Map CD-ROM We originally produced a CD-ROM full of maps for use with Mac/WinAPRS, this CD-ROM contains over 600 megabytes of Maps.
It contains maps of several different resolutions including very high detail street level maps for most of the major metropolitan areas.
This CD-ROM is now out of production but there are many copies of it out there.
We will produce CD-ROMs in the future as needed.
The major areas of maps include
- USGS 1:2,000,000 - All of the US in regional level, state detail level, and state county outlines
- USGS 1:100,000 370 high resolution maps covering most of the major US metropolitan areas
- Digital Chart of the World
- Canada
- Central America
- Greenland
- Japan
- Mexico
- Puerto Rico
- South America
- United States
This CD-ROM is no longer available, however 500 of them were made and you can probably find one to borrow.
Most of these maps are on the WinAPRS FTP site.
Click here to see the Map Outline areas.
The red boxes indicate hi-res street level maps, the blue boxes indicate regional maps.
Map Windows
Both versions support many map windows open at the same time.
On startup, one map window is opened and the first map in the map folder is used.
To create additional maps, use the "NEW MAP WINDOW" command under the "Windows" menu.
Then use the "MAP" menu to select which map to use. You can have as many maps open as you have memory to handle.
When you run out of memory, you will get an warning and it won't open the map. You can also go to the map list window and double click on the name of a map file, it will bring up a new window with that map.
You can select multiple maps into the same window.
Bring up a map window with one map, then go to the MAPS menu and select another map with the CONTROL KEY held down.
It will merge the two maps together in memory (not on disk). You can combine maps up until you run out of memory or 256 maps, whichever comes first.
Holding the SHIFT key down, forces it to create a NEW map window.
Selecting an item from the MAPS menu
- If a MAP WINDOW is currently the FRONT MOST WINDOW (has focus) then the map
in that window is REPLACED with the new one.
- If the front most window is NOT a map window, then a NEW map window
containing that map is opened up.
- If the front window IS a map window and you HOLD DOWN THE CONTROL KEY, it
will add the new map to the current map. This means the two maps are combined in memory into one map.
- If the front window IS a map window and you HOLD DOWN THE SHIFT KEY, then
it will open up a new window.
Map movement
In both versions, you can click on a location in the map and then cause it to zoom-in or zoom-out.
Use page-up and page-down or the '+' and '-' keys.
You can at anytime go back to the default magnification (Home View) by hitting the 'Home' key or the 'h' key.
Once you have zoomed in on a map, you can use left, right, up, and down arrows to move around within the map.
It does NOT automatically switch to another map when you reach the edge of the current map.
Map Boundaries
Display Map Boundaries command will show the outline of all of the maps on the current map window.
This will show you the bounding rectangles of each of the maps.
You can also do this by hitting the 'B' key.
A note when using dos maps. Many of the dos maps will not show up at first when you display the map boundaries, this is because the Mac/WinAPRS maps have a 256 byte header that has ALL of the information needed.
The DOS maps have to be read entirely in before that is known.
Some DOS maps have enough information in the first few lines so that this information can be displayed, many do not.When you open any dos Map (by selecting it from the Map Menu or double clicking from the map list), the boundary information is then saved for future reference.
Map Zooming
You can make MacAPRS / WinAPRS automatically bring up the next higher detail map by double clicking on a point.
For MacAPRS, hold down the option key when double clicking.
For WinAPRS, double click with the RIGHT mouse button.
Map Window Buttons
There are several buttons on the right hand side of the map window, these buttons do different things to the map.
The buttons can be disabled entirely in the GENERAL DISPLAY OPTIONS dialog.
- HM Home
- IN zoom in
- OUT zoom out
- LBL Labels on off (non PM maps)
- LB+
- LB- for non-Precision Mapping maps, turn more labels on / off
- SYM Symbols on / off
- WX Weather mode on/off
- WAY WAY points on / off
- GRID User defined grid (see docs FIRST)
In version 2.2.2/3.2.2, these buttons were changed to ICONs, they still do the same thing.
Precision Mapping Support
For a LONG LONG time, users have been asking, "Can you use Street Atlas Maps", "How can I get better maps of my area?", well the solution is now here.
Precision Mapping Street 3.0 by Chicago Map Corporation is a CD-ROM based mapping system that is just as good or better than any other street mapping product on the market.
The MAIN difference is that the people at Chicago Map Corporation understand that there are developers that need to interface to their products (some of the other map companies don't want to be bothered). They have developed a method whereby I can access the maps directly as part of WinAPRS.
This integration allows WinAPRS to still behave EXACTLY like it normally does with mouse clicking, zooming, displaying overlays, etc. Everything works the same, but the maps are very high detail, very nicely drawn and most important, the detail is dynamic.
In order to use the Precision Mapping option you must install their mapping library that is supplied with WinAPRS.
Installing Precision Mapping OCX
Precision Mapping OCX (C) by Chicago Mapping Corp
The copy of the Precision Mapping OCX is licensed only for use with WinAPRS software.
WinAPRS will work with the Precision Mapping CD-ROM, version 3.0.1 and higher.
This OCX will not work with Windows 3.1, there is currently no work in progress to support Precision Mapping for Windows 3.1.
To install the OCX,
- Unzip the file PMAP_OCX.zip, if you use dos PKUNZIP, make sure to use the -D option (to create a directory)
- Once it is unzipped, run the .BAT file "pmapocx.bat", this can be run at the dos prompt or double clicked from Windows.
- The installer should come up with a dialog box indicating that the OCX has been installed.
- Once it is installed, the ZIP file and the directory can be deleted. The necessary files (MAPOCX.OCX and OC30.DLL) have been copied to your Windows\System directory.
Using Precision Mapping
Once the OCX is installed, simply go to the Windows Menu and do NEW WINDOW PM. This will open up a precision mapping window. Note, you can have MULTIPLE PM map windows open at the same time.
Now go to the OPT button on the lower right of the window, this will allow you to set the DRIVE LETTER for your CD-ROM. Yes, you can copy data to your hard disk on a state by state basis. I will be adding an automatic feature to assist with this function.
Precision Mapping DOES NOT have to be running and in fact does NOT even need to be installed on your hard disk. Just install the OCX and have the CD-ROM in the drive and it works. It does NOT require both programs, it is all done WITHIN WinAPRS.
It has been our experience that Windows95 release 2 is more stable than release 1 for use with Precision Mapping. If you have problems with running out of memory while using this option, check to see which version of Windows 95 you are running.
If you are using a laptop that does not have a CD-ROM you may want to copy some of the Precision Mapping data to your hard drive, here is how to do it
- Create a directory on your hard drive
PMAP30
- Create directories inside of it
- Copy over into these folders the files that you want from the CD-ROM
There is a readme or help file someplace that translates the STATE names into the appropriate FIPS code which is a number, the states are stored in STATES by that name, copy over the ones you want.
Point your CD-ROM drive in WinAPRS PM OPTIONS to the C drive (or drive where you have copied the data)
The file names for the states are as follows (The numbers are FIPS codes)
|
01.ZPX Alabama |
04.ZPX Arizona |
05.ZPX Arkansas |
06.ZPX California |
|
|
08.ZPX Colorado |
09.ZPX Connecticut |
10.ZPX Delaware |
11.ZPX District of Columbia |
|
|
12.ZPX Florida |
13.ZPX Georgia |
15.ZPX ?????????? |
16.ZPX Idaho |
|
|
17.ZPX Illinois |
18.ZPX Indiana |
19.ZPX Iowa |
20.ZPX Kansas |
|
|
21.ZPX Kentucky |
22.ZPX Louisiana |
23.ZPX Maine |
24.ZPX Maryland |
|
|
25.ZPX Massachusetts |
26.ZPX Michigan |
27.ZPX Minnesota |
28.ZPX Mississippi |
|
|
29.ZPX Missouri |
30.ZPX Montana |
31.ZPX Nebraska |
32.ZPX Nevada |
|
|
33.ZPX New Hampshire |
34.ZPX New Jersey |
35.ZPX New Mexico |
36.ZPX New York |
|
|
37.ZPX North Carolina |
38.ZPX North Dakota |
39.ZPX Ohio |
40.ZPX Oklahoma |
|
|
41.ZPX Oregon |
42.ZPX Pennsylvania |
44.ZPX Rhode Island |
45.ZPX South Carolina |
|
|
46.ZPX South Dakota |
47.ZPX Tennessee |
48.ZPX Texas |
49.ZPX Utah |
|
|
50.ZPX Vermont |
51.ZPX Virginia |
53.ZPX Washington |
54.ZPX West Virginia |
|
|
55.ZPX Wisconsin |
56.ZPX Wyoming |
|
Installing PrecIsion Mapping on WindowsNT
The following was provided by Jerry, KB4OAM
- Install PM 3.0/3.5 per the CD instructions
- Create a new \DATA2 folder and a \STATES folder
- Copy the desired 'state' files off the \STATES folder on the CD to the \STATES folder on the hard drive (12.zpx for Florida)
- Download the PMAP30.OCX file from Mark's Rutgers site, and unzip it (using the -d option)
- Edit the PMAPOCX.BAT file, to change all '\windows\' calls to '\winnt\'
- Find a copy of MFCANS32.DLL (from a Win95 machine) and copy it to the \winnt\system\ directory
- Run the PMAPOCX.BAT file (it should complete with a 'success' message)
- Start WinAPRS, and under the 'Windows' pull-down, select 'New Map Prec Map'
- Click on the OPT box, and enter the letter of the hard drive where you earlier created the \states\ folder.
HOME.TXT
In order to get Precision Mapping to automatically come up on a desired location, create a file called HOME.TXT. Place this file in the same directory as the WinAPRS exe file.
#Home.txt must be formatted EXACTLY like this
# ONE tab or space between the key and the argument
# Radius is in arc seconds
LAT 40.3447416667
LON -74.4923555556
RAD 3
The PrecIsion Mapping map window should open up to this view.
To convert that lat lon values, value = degrees + (minutes / 60) + (seconds / 3600) or if you have decimal minutes just value = degrees + (minutes / 60). The RAD value is RADius. This is in arc seconds but a value of 3 is a good place to start.
The HOME key still takes you back to the full view
CONTROL-Home will now take you to this location
Using Images for Maps
Mac/WinAPRS now supports GeoTIFF files.
GeoTiff is a TIFF image with geo-referencing information added.
WinAPRS has been tested with a small sample of GeoTiff files.
The ones referenced in this document work.
I have found some that do not work yet.
These features will be enhanced to include GIF and BMP files and will allow you to do your own calibration of images.
(please note that these images were done with old log files)
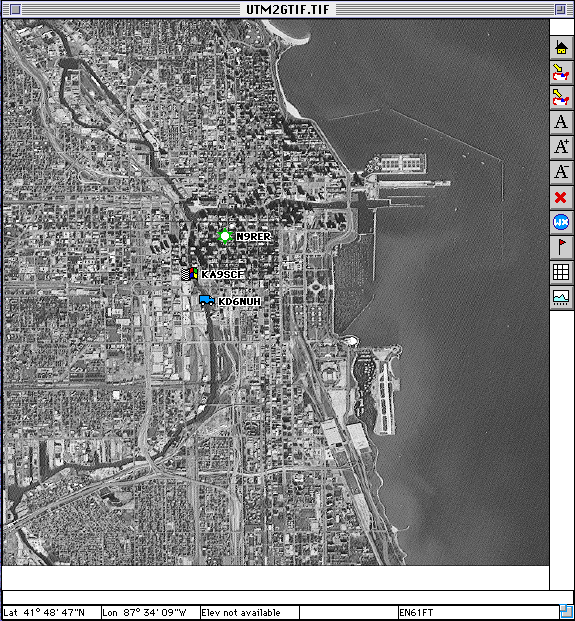
This is a satellite image of Chicago IL. It is a calibrated GEOTIFF file.
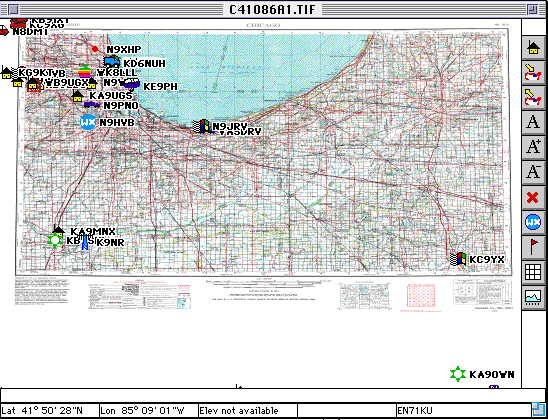
This is a full image of a Chicago DRG (Digital Raster Graphic) file.
The image width =7158, image Height = 5520, which means it occupies 39 megs of RAM just to view.
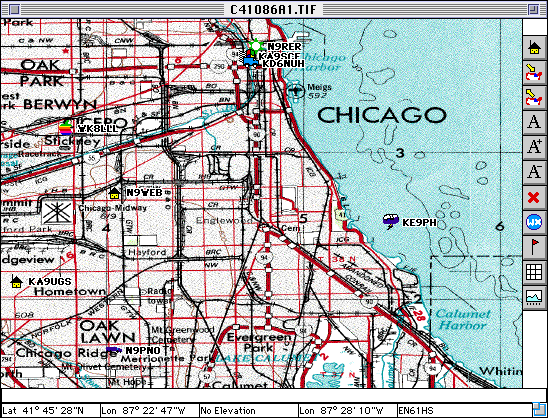
This is a zoomed-in section of the above map
Places to get image map files
How to use non-GeoTiff images
If you have an image and it does not already have the Geo-Reference information, you can add it.
If we have an image "Midwest.gif", place it in the IMAGES directory, then create a file called "Midwest.GEO" and place it
in IMAGES as well. The .GEO file has the following format
FILENAME Midwest.gif
# x y lon lat
TIEPOINT 51 98 -100.286714 44.382867
TIEPOINT 678 450 -87.530247 38.037397
The fields must be separated by tabs, not spaces
The first line refers to which image it is for, this is for future use.
Any line starting with '#' is a comment
You have to have 2 "TIEPOINTs", these associate a lon/lat with any x/y of the image. The X and Y are in
pixels of the IMAGE, the LON and LAT are that LON/LAT values of the POINT specified by X,Y. The more accurate that
you have this, the better the image map will work. The second point MUST be to the right and below the first point.
It is best to have the first point as close to the top left as possible and the second point as close to the bottom
right as possible.
NOTE: The images MUST be ORTHOGONAL, this means that the map lines up square with lat/lon.
URL access
In a similar method, internet URLs can be used to obtain images automatically
URL http://radar.kcci.com/graf/radar1.gif
# This url is from KCCI-TV out of Des Moines, Iowa
# x y lon lat
Tiepoint 85 46 -96.5949388889 43.4924277778
Tiepoint 490 376 -91.4472250000 40.3717138889
These URL files must be placed in the IMAGES folder. They can then be accessed from the WINDOWS / INTELLICAST menu.
Map Server Support
There are several web servers that display map images (gif files) on request. These images are fairly detailed and can be generated for almost any range and area. The two that are currently supported are:
To access these maps, go to any station list, click on a station and click the approriate button at the top of the screen.
The buttons are:
- Open APRS map for station
- Send APRS message to station
These require internet connection
- Open Tiger map for station (US Only), if you select a station outside of the US, it will automatically switch to MapBlast instead
- Open MapBlast map for station
- Look up call sign using University of Arkansas call book server, this is the same service as http://www.ualr.edu/~hamradio/callsign.html
These buttons work on the most recent station clicked on. They do NOT work on multiple stations if more than one is selected. There will be more of these buttons as time goes on.
List Windows

 There are many different types of list windows in MacAPRS / WinAPRS. Each of the windows supplies a list of information organized in a different manner. Some of the information is constant such as the current list of maps. Most of the information is dynamic and will change as stations appear, etc.
There are many different types of list windows in MacAPRS / WinAPRS. Each of the windows supplies a list of information organized in a different manner. Some of the information is constant such as the current list of maps. Most of the information is dynamic and will change as stations appear, etc.
- Message List
- Map List
- Station List
- Flagged Station List
- When Heard List
- Weather List
- History List
- Tracked Station List
- RDF List
- Telemetry List
- Global Labels
- Airport List
- Internal State
- Memory Usage
- Unproto path
Message List: MacAPRS / WinAPRS recognizes standard APRS messages. This window shows all of the messages that have been seen since the program started. Messages TO you will be shown in RED. Messages FROM you will be shown in BLUE until they are ACKnowledged, then they will be shown in GREEN. Bulletins will be shown in DARK BLUE. Station ID's will be shown in light BLUE. Other messages will be shown in BLACK. Selecting a message and typing 'R' will REPLY to that message, already filling in the destination call sign. You can click on the column headers and the messages will then be sorted by that column.
When the message buffer is full, it will delete the FIRST HALF of the messages EXCEPT for any messages that are actually to you. It will continue to do this as every time the message buffer fills up. In other words, you can go away for the weekend (or a whole week) and come back and ALL of the messages that were sent to YOU will still be there, all of the recent messages will still be there. You don't lose anything important and you don't have to remember to clear the message list.
Map List: The Map list is a list of all of the currently available maps: this is NOT to be confused
with "MAPLIST.DAT" from DOS-APRS.
This list shows the name of the map file, the name of the map, the number of points, the number of labels, the creator and the type (Mac/Win or DOS).
For DOS-APRS maps, the number of points and the number of labels is NOT available unless you read the entire map in and count them.
Therefore this information is not available in the beginning.
As soon as you use a particular map, that information is updated in the map list window so the contents of the window will change.
While talking to several of the beta testers of WinAPRS, I have mentioned the "Map List".
This refers to THIS window, NOT the menu list.
You can double click or hit the return / enter key and a new map window with the selected map will be created. Remember, you can have as many maps open as you have memory to handle.
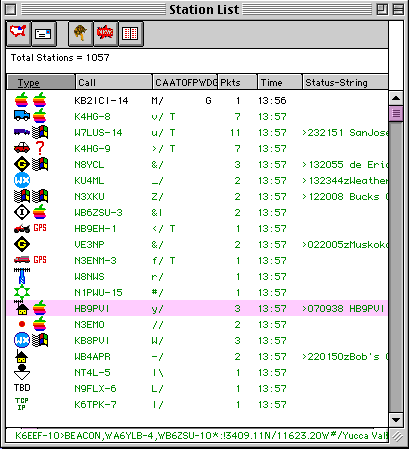
Station List: This window shows all of the stations seen since the program started. The list includes the ICON of the station, a second ICON if the station has reported more than one type, i.e. QTH and WEATHER, call sign, number of packets, and station ID if any. While in this window, you can Double Click on a station to bring up the Station Info Window for that station. You can also use the up-down arrow keys and then hit RETURN or ENTER to bring up a Station Info Window. Page-Up and Page-Down work also.
Note: If the internal buffers overflow, the packet list will reset back to zero. Therefore, this window might say that you have received a large number of packets from a station and not show any. Don't let this alarm you.
CAATOFPWDG
||||||||||
|||||||||+- GPS DESTINATION FLAG (ONLY ONE IN LIST)
||||||||+-- Danger Flag Type 'D' in any of the lists
|||||||+--- Warning Flag Type 'W' in any of the lists
||||||+---- Message Pending Counter (+ if greater than 9)
|||||+----- Flagged Flag Type 'F' in any of the lists
||||+------ Object Flag
|||+------- Tracked Flag Type 'T' in any of the lists
||+-------- Alarm Flag Type 'A' in any of the lists
|+--------- Adjective Character
+---------- Icon Character
History List: The history list shows ALL of the packets received. This can get to be a very long list. When it fills up, it dumps the buffer and starts over.
Weather List: This window shows data from Weather stations and includes station type, call, time, temperature, rain fall, pressure, wind speed and direction, and weather alarms.
Flagged Station List: is a list of stations that you have "flagged".
You can flag a station by going to the Station List window, selecting a station, and hitting the 'F' key.
This allows you to keep track of stations that you are interested in without having to scroll through the entire list.
The FLAGGED concept is so that you can have a list of "STATIONS OF INTEREST".
For example, you might be running an event, other hams are interested in the event so you leave it on the normal APRS frequency, however, you, running the event want to be able to ignore the other stations on the map, in your list, etc.
Flag these stations, bring up the FLAGGED list and set DISPLAY FLAGGED ONLY and all of the others "disappear" They are still there and are in the other lists but are out of your way.
When List: Displays a window showing when the stations in the Station List were heard.
Tracked Station List: Shows the moving stations that are being tracked.
RDF List: Shows a list of stations reporting Radio Direction Finding information
Telemetry List: The APRS protocol defines an ability to have telemetry data transmitted from something like a balloon.
This window will display that information if any is available.
Internal State: This window shows the values of important settings inside the program.
This is different from the settings dialog boxes because they can be misleading at times.
This window allows you to look at all of the important internals in one place and will allow us to better assist users in case of problems.
Memory Usage: For diagnostics mainly, to help determine when and where memory leaks are occurring, not very useful for general use.
Unproto Path: This window shows a list of all of the stations showing the path that was used for their data to get to you.
This is useful in looking at which digis get used most and is the first step in supporting automatic path selection for responding back to other stations.
Column 1 shows the station ID (call sign), station 2 is a "Y" if the station was heard direct, the rest of the columns are the digis, starting with the station callsign in the order they were seen. This window can be sorted by any column by clicking on the heading for that column. Stations that were heard direct are displayed in green.
Airport List: If you have the file "Airport.dat" or "Airport.data" in you DATA directory, then you can display most of the airports in the world. Select AIRPORTS under the DISPLAY menu, this will draw all of the air ports in the list on the current map. This is a temporary display only and the airports will disappear the next time the map is redrawn. If you hold down the option key for Mac or the Control key for Windows, it will display the airport 3 letter code as well.
You can look at the entire list by selecting AIRPORT LIST under the LISTS menu. This will display the entire list showing the airport code, city, lat / lon and elevation. The elevation data is not present for all of the airports but most of them. You can sort the list by clicking on any of the column headings. This can be interesting when you do a display airports because they will be displayed on the map in the same order they appear in the list. i.e. sort by elevation then do a display for the entire USA map.
If you double click on an airport in this list, you will be switched to the best map currently open that contains that airport and shown where on that map the airport is. If no map contains the airport, it will beep.
The airport data file can be found on the CD-ROM that we produced or on the FTP site, it must be placed in the DATA directory and MUST be named "AIRPORTS.DAT" for Windows and "AIRPORTS.DATA" for Mac.
Logging
There are several different logging options. All are turned on and off from the LOGGING menu.
- Station Logging - this logs ONE entry for each station seen.
- APRS Logging - this logs all traffic coming in exactly the way it is received from the TNC.
- NMEA Logging - this logs data from your GPS unit. This is used to create NMEA files while you are in motion. This data is saved in NMEA format.
- Local Weather Logging - once every 5 minutes, information from the LOCAL weather station input is stored to disk. This is currently in binary format.
- Message Logging - this logs ALL messages.
- Local RDF Logging - This writes out data from your LOCAL RDF unit.
Menu Commands
File Menu
- Open The file open command lets you open a log file.
- New Map Window will open a new window with a map display
- Save will save a file, each of the LIST windows will save out a log file with the information contained in that list, the MAP window will save out a new map. This is for when you modify the labels in a map. (saving of maps is not finished for WinAPRS).
- Close Closes the current window
- Quit Just what it says
Edit Menu
- Edit/Add Station Will allow you to edit or add a station object.
- Edit/Add Label Will allow you to edit or add map labels.
- Clear Stations This clears ALL stations from memory.
Settings Menu
Logging Menu
- The Logging menu is covered in the Logging section above
Map Menu
- Display Map Boundaries This will show outlines of all of the current maps.
- Maps... You can select a new map to be the displayed in the current window. On Windows, this menu does not scroll so you may have to go to the Map list to see all of your maps.
Display Menu
Station Alarms
There are many times when you want to be notified about the movements of a moving station. For example, when it is within 5 miles of your location, 1 mile of your location, or maybe every time it moves.
For example, if you set the ALARM flag, Mac/WinAPRS will beep every time a packet is heard from that station. WARNING flag will beep if a packet is heard from the station within the WARNING radius set in APRS SETTINGS. Danger will beep if the station is within the DANGER radius.
Refer to Key Board Shortcuts (station list window) shortcuts and to Special Stations
Terminal Window
 Under the "Windows" menu, select the terminal window command. This will bring up a terminal window that will allow you to talk directly to your TNC or other port. It will connect to whichever port you have open. If you do not have any port open, it will not let you open the terminal window. During the time that the terminal window is open, APRS data STILL gets processed. If the Terminal Window is the FRONT MOST WINDOW, then WinAPRS will NOT output any commands or strings to the TNC. If the terminal window is not the currently active window, then WinAPRS will output as normal. At ALL times, the INPUT from the port is still processed normally by WinAPRS so you do not lose any data.
Under the "Windows" menu, select the terminal window command. This will bring up a terminal window that will allow you to talk directly to your TNC or other port. It will connect to whichever port you have open. If you do not have any port open, it will not let you open the terminal window. During the time that the terminal window is open, APRS data STILL gets processed. If the Terminal Window is the FRONT MOST WINDOW, then WinAPRS will NOT output any commands or strings to the TNC. If the terminal window is not the currently active window, then WinAPRS will output as normal. At ALL times, the INPUT from the port is still processed normally by WinAPRS so you do not lose any data.
Messages
APRS users can send one line messages to other APRS users. These messages are then acked from the other station.
The messages can viewed in the MESSAGE LIST. Messages to you are red, messages from you start out blue and turn green when they are acked.
A message is sent out normally 4 times or until it is acked. The number of times is settable in one of the settings dialogs (default = 4)
However, after it has been sent 4 times, if I see a packet FROM the station that the message is to, it will automatically go out again.
Scenario. I have an occasional band opening to a station that I like to talk to.
I am keyboarding away to this station and the band opening dies.
I have 5 or 6 messages queued up waiting to go to him. 24 hours later, the band opening opens back up
for one minute and I see one packet from him, poof, the first message goes out, his ack comes back, the second message goes out, his ack comes back, bang bang bang, all of the messages go out real quick during the band opening.
We have seen this happen several times.
It could also happen if the person was mobile and he came within ear shot of a distant Igate.
Bulletins and Announcements
- Bulletins are SHORT TERM announcements that are TIME critical.
Bulletins are sent ONCE EVERY 20 minutes for 4 (FOUR) hours.. Then STOP.
- Announcements are longer-term items that are NOT time critical.
Announcements are sent once an hour and are sent for 4 (FOUR) days, then STOP.
Messages, Bulletins, and Announcements can be re-queued by CLEARING them in the MESSAGE window. They can also be canceled by deleting them
You CLEAR messages by selecting the message and hitting 'X' or '\' or the
CLEAR key on a Macintosh.
To DELETE a message, select it and hit DELETE or BACKSPACE.
Starting with version 2.2.2 (Win)/ 3.2.2 (Mac) message delivery is SEQUENTIAL instead of PARALLEL.
In the message list there is an ACK column, this will be blank except for messages FROM YOU. Q means the message is QUEUED, A means its been ACKED, and QB, means QUEUED and BLOCKED, When the PREVIOUS message to THAT station gets acked, the NEXT message gets UN-BLOCKED and will go out.
This does work and works well.
If you have a good link, the messages will go through very fast
Refer to Key Board Shortcuts page for all of the options in the message window.
APRS Objects
You can add an object by clicking anywhere on a map, then selecting the "edit/add object" command from the EDIT menu. Fill out the information. You can change the location by clicking on the object, then "edit/add object" it again, OR, you can hold down the Command/Alt key and drag it to the new location.
Creating: When you create an object, if you want it to be transmitted out so others see it, make sure that the OBJECT setting in the "Position Rate Settings" "Object reporting rate" dialog box is something other than 0 (the default) for the band you desire. A good recommended value is 30 minutes or higher. You also need to make the Object active by checking the "Object active" box and the "VHF" or "HF" box in the "edit/add object" dialog box.
Moving: To move an object on the screen, hold down the Command Key (Mac) / Alt Key (Windows) and click on the station, you can then drag it to a new location. If someone else moves the object your copy will become inactive and you will need to re-activate if you want to move it again and have it transmitted. To re-activate it you must click on the object once and the edit/add object from the edit menu again and set the HF/VHF and Active flags. The idea here is that only one station can really send the location of a given object at a time.
Removing: To delete an object, go to the station list window, then select the object to be deleted and hit the delete key or backspace key(Windows).
Additional notes: The objects are uniquely identified by the Callsign field in the edit/add object menu. If you use the same callsign name to try to create a new object you will not get a warning. The old object will be deleted and the new one will appear. This is useful if you need to relocate an object since you do not need to delete the old one.
Fancy symbols for objects can be selected in the edit/add objects menu STATION TYPE field. To view the possable symbols use the LIST -> SYMBOLS LIST function or just type random characters in this field till you find something you like. (- minus sign is a home QTH).
HSP Support
HSP (Hardware Single Port) was designed to solve the problem of only having one serial port and the need for both TNC and GPS input. This is done with a special cable that has a simple transistor switching circuit. The DTR (Data Terminal Ready) line from the computer is used to switch this circuit allow for input from two different devices. It only switches the data into the computer, not out of the computer.
HSP is supported on the VHF TNC input and the HF TNC ports only. To enable this, go to the Serial Port dialog box and set the appropriate check box. HSP is turned on (switched) for 4 seconds of each minute. This has been tested with the PacComm HSP cable.
Please note that the PacComm HSP cable needs +5v on Pin 6, the Handi-packet does not provide this. You might need to install a jumper between pin 6 and pin 8 of the DB9 on the TNC. Please refer to the schematics or customer support of your TNC manufacturer.
HSP does NOT support weather input.
The Mac version does not support HSP and is not likely to. To get around this problem use a TNC with a GPS input such as the Paccomm Pico-Packet.
Audio Alarms (sound files)
When various events happen, audio alarms are played to announce that fact. These alarms can be turned off under settings. For MacAPRS, these sounds are stored as 'SND ' resources within the file, for WinAPRS, they are external .WAV files. These files MUST be in a directory called SOUNDS which MUST be in the same directory as WinAPRS.exe
Wave File ---- action causing alarm
- GPSAlarm.wav --- GPS alarm
- BandOpen.wav --- Band Opening
- Bulletin.wav --- New Bulletin
- DeltTemp.wav --- Delta Temperature alarm
- LowTemp.wav --- Low Temperature alarm
- HiTemp.wav --- Hi Temperature alarm
- HiWind.wav --- High wind alarm
- Moved.wav --- Station Moved
- NewMail.wav --- New Message
- NewStat.wav --- New Station
- TNCConn.wav --- TNC Connected
- SelQuery.wav --- Selective Query
- ProxWarn.wav --- Proximity Warning
- ProxDang.wav --- Proximity Danger
- WxBultn.wav --- Weather Bulletin (NWS weather warning / watch / advisory)
Mouse Down shortcuts
These "modifiers" affect the operation of mouse down, mainly in the map window. By holding down the specified key, you can invoke many other functions. For most of these operations, the key must be held down the entire time.
MAP Window
- Click and drag with Option Key (Mac) / Right Button (Windows) ---
Set new map boundaries, this will zoom into a new level as specified by the drag rectangle.
- Command Key (Mac) / Alt Key (Windows) ---
Drag an object to a new location.
- Control Key - Selective query, click on a point and drag out a radius, the result will transmit a selective query for the defined area.
- Double click with Right button (Win) / Option key (Mac) -- Search through the maps and find the next best map (smaller area) for the clicked location.
- Double click with shift key and Right button (Win) / Option key (Mac) -- Search through the maps and find the next larger area map for the clicked location.
- Double click with control key and Right button (Win) / Option key (Mac) -- Search through the maps and find the smallest area map for the clicked location.
List Windows
- Double click - For all windows that list stations EXCEPT the weather, list, double clicking will bring up the station info window for that station. For the weather list, it will bring up a weather chart.
- Option double click - will show the station on the best currently loaded map. If no map is currently open that contains that station, it will beep.
Function Key Shortcuts
Function keys work for Mac as well starting with version 3.2.2
- F1 - Open Help window, the file WAPRSdoc.htm must be in the DOCS folder for this to work.
- F2 - Send Position
- F3 - Find in current window (map or list)
- CTRL-F4 - Close current window
- F5 - refresh current window
- F6 - Go to next window
- F7 - New message
- Cntrl-A - Select All, List windows only
- Cntrl-F - Find
- Cntrl-G - Find again
- Cntrl-C - Copy (not implemented in all windows)
- Cntrl-S - Save, only implemented in list windows
- Cntrl-W - Close current window
Keyboard shortcuts
MAP Window
List Windows
- "PageUp" -- Scroll back in the list
- "PageDown" -- Scroll forward in the list
- "Home" -- Go to top of list
- "End" -- Go to bottom of list
- Up / Down arrows -- Move up or down 1 line
- Return -- Selecting a line, then hitting return will do the same as double clicking on the line. In most (not all) list windows, double clicking on a line will bring up more information such as double clicking in the list window will bring up the station info window for that station.
Station List Window
- "A" -- Alarm, sets movement alarm for the currently selected station.
- "D" -- Danger, sets danger alarm for the currently selected station.
- "W" -- Warning, sets warning alarm for the currently selected station.
- "Delete" -- If you have added an object, you can delete that object by selecting it and then hitting the delete key
Message List Window
- "A" -- AGAIN If CAPS LOCK is not down, it RE-PLAYS the message via the Macintosh Text To Speech (Mac Only)
- "Clear" or "X" or "\"-- Clears the counter(s) allowing the message to keep on trying to be sent.
- "F" -- FORWARD Brings up a new-message dialog box with the text of the CURRENT message in the text box and the cursor in the TO field to allow you to type in a new recipient.
- "N" -- Send this message again NOW, only if it was originated by you. Does not matter if the message has been acked or not.
- "R" -- REPLY Brings up a new-message dialog box pre-addressed to the SENDER of the message. The cursor is in the TEXT box ready for you to type
- "S" -- SEND Brings up a new-message dialog box pre-addressed to the RECEIVER of the message. The cursor is in the TEXT box ready for you to type
- "Delete" or "BackSpace" -- Deletes the message, sets the FLAG (changes to MAGENTA) so the message won't be sent any more
- "=" -- Sets the message to ACKNOWLEDGED (changes to GREEN)
Weather Chart
- "ZP" Zero Pressure
- "ZR" Zero Rain
- "ZT" Zero Temperature
- "ZW" Zero Wind
- "ZZ" Refresh the screen, re-calculating the minimums and maximums used for auto-scaling the graphs
Printing
 On the Mac you can print any and all windows. The print command applies to the current window. The map windows will be resized to fit the paper of the currently selected printer so they should never take up more than one page on the output. Also the print code has been written so that it works well with pen plotters and will take proper advantage of the large print area of a large pen plotter.
On the Mac you can print any and all windows. The print command applies to the current window. The map windows will be resized to fit the paper of the currently selected printer so they should never take up more than one page on the output. Also the print code has been written so that it works well with pen plotters and will take proper advantage of the large print area of a large pen plotter.
 WinAPRS can print the list windows, map windows do not print at this time.
WinAPRS can print the list windows, map windows do not print at this time.
Map Labels List
A feature to help locate roads on the maps has been implemented. Under LIST menu select MAP LABELS LIST
- Then select a map, preferably the same one you are using.
- Now you should have a list of labels, it is possible that there are no labels for a map,
- Double click on a label, and it will show you where the street is, if it beeps, it is not currently visible on any open map
FIND
Find can be a VERY useful tool, with it you can find the location of a zip code, of an airport, of an existing station or of any ham listed in a call book database.
In the map window you can search for these items
- Airports
- Gridsquares
- Call signs of APRS stations
- Call signs of any ham (call book CD-ROM required)
- Zipcodes
In the station lists you can search for call signs, in the airport list you can search for a city name, in the history list you can search for any text.
Map Display Options
Under the DISPLAY menu is the Map Display Options. This allows you to set many options for how maps display including:
- Background color
- Text Color
- Always display Civil Air Patrol Search And Rescue grids
- Always display ARRL Gridsquares
- Label color for Global labels and for DOS Map labels
These options can be applied to the current map, all maps, or set as default.
CD-ROM call sign database support
MacAPRS / WinAPRS can take advantage of call sign databases on CD-ROM. Under settings menu, select CALLBOOK, there is a pop-up menu to select which CD-ROM database you want to use. When selected, this automatically fills in the paths for the files. If you have copied items to your hard disk you can manually change these paths. For Windows, you must set the drive letter for your CD-ROM drive.
The following CD-ROMs are supported:
- Buckmaster - both the older ones US only and the new format, (starting with October 95)
- Amsoft
- Percon
- SAMS
- QRZ
- The Flying Horse CD-ROM is NOT supported. They have not agreed to supply us with the information that we need in order to support it.
Some of the CD-ROMs have to have an index created in order to use them. To create the database, go to the CALLBOOK DATABASE under SETTINGS menu. Select the desired database from the popup menu, at the bottom of the dialog box is a button that says MAKE: CallSign index. Select this button and it will create the index.
PLEASE NOTE: This can take a while and generates an index that is typically 3 megabytes. For WinAPRS this cannot be aborted, for MacAPRS, Command-Period will abort it. For WinAPRS with a 4X CD-ROM drive on a 100 megahertz Pentium it took about 4 minutes each to create the QRZ and SAMS index files.
Each time you get a new CD-ROM, simply throw away the old index file and re-create it. You do not have to download it off of the internet. The index files are compatible between Mac and Windows, so if you create the database on one machine, you can copy it to another of the other type.
The index file is automatically created in the DATA folder inside of your WinAPRS folder. For the Buckmaster CD-ROM, the index is already on the CD-ROM and is left there.
Below is a table for which databases need indexes
| Callbook Database Indexes
|
|---|
| CD-ROM |
Index required |
MacAPRS |
WinAPRS |
comment |
| Buckmaster |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
Included on CD-ROM |
| QRZ |
Yes |
Tested |
Tested |
About 3.8 meg |
| SAMS |
Yes |
Tested |
Tested |
About 3.8 meg |
| AMSOFT |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
- |
| PERCON |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
- |
| FCC Database |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Installing the new (2000) FCC database
Sometime in 1999 the FCC changed the format of the database, below are the instructions to download the new database and make it work with WinAPS/MacAPRS/X-APRS.
The FCC database currently DOES work on X-APRS, but you need to create the index on another platform (Mac or Windows).
Check our FTP server or email kb2ici@amsat.org to request the index.
UNPROTO path
Probably the biggest single confusion about APRS is the UNPROTO path.
This is the path that the TNC is set to use for unconnected packets.
(All APRS communications is via unconnected packets known as UI frames).
There is a window that shows the paths that each station uses (under LIST WINDOWS).
This can be very helpful to see what others in your area are using.
There are several guidelines when setting your unproto path.
- NEVER use 3 of the same thing such as WIDE,WIDE,WIDE.
This will cause TREMENDOUS amounts of excess re-transmission of packets.
In some cases enough to cripple a network.
- Including a "GATE" in your path will allow your packets to GATEWAY from VHF to HF or vise-versa.
Do NOT put more than one GATE in your path.
- RELAY should be used if you are new station, but after you figure out which path to use, then discontinue using RELAY at all.
- RELAY should NEVER be anywhere EXCEPT the first item in the proto path.
- NEVER use RELAY after a WIDE.
- In a given area, there should not be more than 2 digis with an alias of RELAY.
More than that can cause a given packet for a new user or mobile user to be repeated 27 times.
If you can hear 2 digis with an alias of RELAY, DO NOT set yours to RELAY.
- In a given area, there should not be more than 2 digis with an alias of WIDE, if you can hear more than one WIDE, DON'T set your alias to WIDE.
- RELAY,WIDE,WIDE should NEVER be used by a home station, however it is a good choice for a MOBILE station.
Discussion on unproto paths
This section is meant to familiarize you with the concepts of APRS operations so that you can get running with maximum efficiency and minimum disruption to other stations in the network.
The information in this section applies to all versions of APRS.
Since APRS stations do not "connect" to each other as in a typical packet QSO, but rely on "unconnected" packets, the only way to get your data to others beyond your station's reach is through the use of digipeaters.
Users of APRS have standardized on a scheme for digipeating that requires some explanation.
Just as it is advantageous to have a packet node or a repeater located in a high spot with great coverage, so it is with digipeaters.
In APRS terminology, such a wide-coverage digi is called a WIDE.
In any given area, there should only be one WIDE, and that station should be able to work the adjacent WIDEs and should operate 24 hours a day.
Don't be an "ego-WIDE"; that is, setting yourself up as a WIDE when you cannot provide the functionality of a true wide or are in an area already served by a proper WIDE.
You will only cause problems on the network and earn the wrath of those whose traffic you are affecting.
Of course, we cannot expect every station in a given area (mobiles especially) to be able to work a WIDE (especially if they are on the move), so to assist those stations to make a WIDE, there are RELAY stations.
A RELAY station can be any station that can work one or more WIDEs reliably.
There should be only one RELAY in a given area that can work a given WIDE; the same "ego-WIDE" caution applies here. Of course, if two (or more) stations overlap in coverage slightly but primarily cover differing areas, the benefits of covering the extra area might outweigh the extra traffic and collisions on frequency. This is where those Ham "experimenter" skills come into play. Remember, when all is said and done, we're here to innovate and experiment while (hopefully) having fun. Don't get too obsessive or relaxed with any of the guidelines herein.
So now, as a user, needing to choose a path to digi your packets through, what should you use? Initially, set your UNPROTO path to RELAY (see your program docs for info on how to do this). Once you see some stations appear on your map, see who you can hear directly using the DIGI or PROTOPATH list. Can you hear a WIDE directly? If so, change your UNPROTO path to WIDE (or WIDE,WIDE if you want to go two hops). If not, and you can work a RELAY directly, try RELAY,WIDE (or RELAY,WIDE,WIDE).
You may also see a GATE station. GATEs pass traffic from HF nets to VHF nets. GATEs should never be used from VHF to HF - this will have real bad implications for the HF net (perhaps even crippling the entire net). The 300 baud traffic of HF should pose no problem on the VHF 1200 baud net, but the reverse is certainly not true.
DIGI PATH DO'S AND DON'TS:
-
DO use a WIDE over a RELAY if you can work one directly.
- DO make yourself a RELAY if you can work a WIDE directly and no one close to you is doing the same.
- DO check your DIGI or PROTOPATH lists to see what stations you can work directly.
- DO use actual callsigns if appropriate, especially if you can see more than one RELAY but not a WIDE. Example path: N2XYZ,WIDE,WIDE
- DON'T use any of the following paths:
- WIDE,WIDE,WIDE: After the second WIDE transmits your packet, the first one will pick it up and re-transmit it a second time. This snowballs and causes lots of wasted bandwidth.
- WIDE,RELAY: Causes ALL home RELAY stations to retransmit your packets. BAD idea.
- GATE: Mentioned above.
- DON'T put up a WIDE unless you truly have wide coverage and there are no other WIDEs in your area, and unless you plan to let it run 24 hours a day.
- DON'T take all of these as gospel. Circumstances vary from location to location and you may need to bend or break these rules-of-thumb in your area. But DO check with your APRS neighbors first!
Alternate Paths for VHF and HF
As explained in the section above, you have a PATH setting for unconnected packets. This path is normally something like "APRSW via RELAY,WIDE". This path is set in the TNC settings dialog box in unser the SETTINGS menu. In order to change the path, the TNC has to be taken out of CONVERSE mode, sent the new command, then put back in CONVERSE mode. This is why the changing of paths was not implemented in earlier versions. When you make a change, it stays in affect till you change it back. If you close the TNC port and reopen, or restart WinAPRS, it will go back to the value in the TNC settings dialog box.
To use this function, you need a file called "ALTPATHS.TXT", this is a simple text file as follows
relay,wide
wide,wide
wide,gate
On startup, WinAPRS reads this file and creates 2 sub-menus under SETTINGS, one for VHF and one for the HF port. There is also an "OTHER" option that allows you to type in a path. The "APRSW VIA" is inserted automatically.
You can add as many options to this text file as you need to.
Setting up a Gateway
It is possible to set up a station that has radios on both VHF and HF and have it "gate" packets between the two.
Packets with "GATE" in their path will then be passed on to the other band.
The purpose of a HF to VHF gateways is to permit VHF local area APRS nets to see mobile stations on HF nets.
VHF stations in general should NOT gate onto HF, but HF stations should gate onto VHF, this is because of the slower bandwidth of HF.
Of course in some situations, gating onto HF may be important.
Several TNCs such as the AEA DSP-2232 and the KAM Plus have this ability built into the TNC.
A gateway gates both directions, if someone on VHF has GATE in their path, your station will GATE them to HF, if someone on HF has GATE in their path, your station will GATE them to VHF.
If you set your station up as a gateway you are on BOTH HF and VHF, YOU do not need to have GATE in your path at all.
Overlay Files
There are many times when you need a graphical display of a large number of stationary objects.
These would be items that are too numerous to transmit and are intended for local references.
Examples are list of digi-peaters, list of repeaters, list of airplane crash sites for Search And Rescue.
Mac/WinAPRS supports POS files.
This is the same format as dos *.POS files.
To use them goto FILE menu OPEN command. Select any file with a a POS extension.
This loads the file into memory, then type "O" for Overlay on any map window and the entire list of items will be displayed.
You can create an OVERLAYS folder and place all overlay files in this directory.
The items will be added to a pop-up menu in the DISPLAY menu for quick access to all of the files that you have in this folder.
Internet Operations
Mac/WinAPRS supports a variety of Internet operations. In no way is Internet access required, it is just used to enhance the overall APRS community.
Types of operations
- Connecting to an existing APRS server to "see" more of what is going on around the country/world
- Setting up an Internet Gateway (IGate) so that others on the net and around the country can see what's in your area.
- Enabling your IGate to pass messages from other stations out to hams that may be in your area that are not on the internet.
- Setting your station to be an APRS server allowing others to connect to you
- Forwarding special format APRS messages on as Internet Email
Each of these are discussed below, please read over and understand each of the operations before trying to implement any of them on your station.
TCP/IP Connections
There are several versions of APRS servers (reflectors) on the internet, these systems listen to a TNC and re-broadcast the information from the TNC to anyone who has connected in via TELNET protocol.
This allows people to see APRS information from other parts of the country.
Steve Dimse has written APRSserve which is the most sophisticated of these servers.
To connect to these servers, you have to be connected to the internet, either directly or via dialup (PPP or SLIP).
Also you must have a file called "APRSserv.txt", this contains the names and port numbers for the various APRS reflectors.
Of course you MUST also have TCP/IP installed and configured.
If you have internet access and can run Netscape or other Web browser, then this part is already done.
To open the connection, simply select the server you want to connect to from the TCP/IP connections sub menu under SETTINGS menu.
Then sit back and watch, stations counts greater than 700 are common.
Mac/WinARS can also operate as an APRS server, it allows connections on port 14439 or port 23.
When you connect you get a dump of the current station list from the server.
TCP/IP to RF Gateways (IGate)
With the introduction of Internet to the APRS picture, the next logical step was taking data from the internet back out over RF.
Of course there are several problems in doing this, the first of which is legal.
Data MUST be originated by a licensed ham in order to be transmitted over the air.
This was taken care of in this implementation.
Mac/WinAPRS, if attached to both a TNC and the internet can in addition to feeding data from RF to the internet relay messages from the internet back out to RF.
The is done by turning on the 3rd Party Message Forwarding option under TCP Connections in the SETTINGS menu.
With 3rd party messaging enabled, whenever a message comes in, it is inspected for several things, if the message meets these criteria
- It came from internet
- The originator was seen on internet and NOT seen locally
- The destination station is LOCAL, Local is defined as 3 hops or less and NOT through a GATE
If a message passes all of these tests, it is formatted as 3rd party APRS traffic and sent out over the air.
Ideally the intended station would then hear this message and send out an ACK.
The security of the APRSserve requires that we can verify that the people feeding data are valid hams. This is a FCC requirement and we were very careful about the implementation. If you are not registered, then APRSserve cannot accept the data that you feed. It will accept your own data and send it out to the other users on the internet. However it modifies your path so that other IGates (Internet to RF gateways) can recognize that the data has not been verified and thus NOT send it back to RF
We apologize about this, we really don't like having to require registration for this but to protect us from some non-ham doing malicious things over the air, we had to.
Possible problems: If you are running 2 different stations, one on TCP and one on RF, they MUST have different SSIDs for the 2 stations.
In order for an IGate to send a message to a station on it has to hear you as local, for Mac/WinAPRS that is defined as NOT through a GATE and through 3 or less hops.
On a station operating as an IGATE, you can bring up the PROTO PATH LIST and see if it thinks you are local. If it does NOT, it will not forward to you. It also has to have heard you on RF. If it has only heard you through TCP it will not gate to you either.
There is an IGATE list that shows all stations that are acting as IGates, additionally on any map window, typing "I" will display a red circle around all of the IGates, thus helping to locate IGate stations for message traffic.
Special Stations
There are several settings for a station seen on the air that you may want to always be set. Normally to set these options for a given station, you must wait to see it first, then go to the station list and manually set the flag. These include warning and alarm flags.
For many people operating IGates, there may be one or more stations that you always want to have IGated to the local VHF frequency, maybe someone that travels with a tracker box a lot.
A feature to allow setting of options for a station has been added. To do this create a text file called "Stations.txt", place the call signs, one on each line, they MUST be upper case and they MUST include the SSID for the station.
- IGATE - always IGate ALL packets from this station
- WARNING - set the warning flag for this station
- DANGER - set the danger flag for this station
- ALARM - set the alarm flag for this station
- FLAGGED - set the flagged flag for this station
- TRACK - set the track flag to track moving objects. Auto-track can be turned on to track all stations but you may not want to track all for memory conservation.
Example
There is no list window to show these stations and there only indicator is in the TCP server status window, there is a entry that tells you the number of special stations. There is no limit to the number of entries in this file. Please be sure to limit the number of IGATES to just a few so that you do not cluter the local RF network.
IGate EMail operations
Note: This may not be enabled in the released version but should be available as a service
The IGate can also forward specialty formatted APRS messages to the internet as EMail.
Send a message to EMAIL, the first part of the message (up to the first space) is the email address, the rest of it is the content
kb2ici@amsat.org One Line msg format email from APRS
Details
- When an IGate server sees the message and has EMAIL enabled, it will ACK the message
- When the same IGate then completes the SMTP protocol, it sends BACK to the APRS station the final result status as an on-air APRS message
- The IGate station ONLY forwards messages it heard on the air, therefore any message that is echoed out over the internet is NOT picked up by 20 IGates and sent 20 times.
- In MANY cases a user still may get more than one copy of a message if more than one IGate hears the packet on RF. An Igate can have Email disabled.
- Not the location in the email. This is the State, City, County information that is entered in the station settings. It is important that the IGates have this information entered. It will give some idea where the person sending the message was located at the time.
- The EMail is implemented through SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). You must have an SMTP server available to talk to in order for your IGate to forward email properly. Additionally, some SMTP servers are restricted in where they can forward email to. Most likely the SMTP server that you use for your normal mail from your local ISP will work fine. The ones that might be problems are SMTP servers within corporations or universities, they sometimes have restrictions. For those that need to know, SMTP uses TCP port 25.
The format of the email will be
Subject: APRS Message from KB2ICI
One Line msg format email from APRS
--------------------------
Message received by MacAPRS IGate station KB2ICI-14
Located in NO BRUNSWICK, NJ
APRS path = KB2ICI>APRS
Weather Options
There are several features of Mac/WinAPRS boundaries tailored to weather watching, these include:
- Weather station input and transmission (see section on weather station input)
- Weather station display (see below)
- Display of all National Weather Station locations. dosAPRS supports a file called "NWSPOSNS.POS", or the older version "NWSPOSNS.DAT", this is a list of NWS stations across the country (over 700 of them). On any map window, you can type "N" and it will display these locations with their 3 or 4 letter name. At present this is not very useful but it was added for some weather functionality that is being worked on and because it is a feature of dosAPRS.
- Weather maps from www.intellicast.com
Weather Station Input

 MacAPRS and WinAPRS support several weather stations. Currently supported units are:
MacAPRS and WinAPRS support several weather stations. Currently supported units are:
- MANUAL
- Peet Bros Ultimeter-II
- Peet Bros U-2000
- Peet Bros 500
- Heathkit 5001
- Davis
- Radio Shack WX-200
- Texas Wx Station
- Maximum WeatherMAX
- Capricorn II
- Davis Vantage Pro - http://www.davisnet.com
- Weather File input Weather Display - http://www.weather-display.com
When weather data comes in from any of the supported units it is stored internally and available for local display. You can display the last 24 hours in the "24 Hour Weather Chart". The current data is then available to output over the air either manually (by selecting the TRANSMIT WEATHER menu) or automatically from the weather options dialog box.
In order for Mac/WinAPRS to transmit the weather, the data MUST be less than 90 minutes old. For manual stations, this means that you have to have set it from the dialog box within the last 90 minutes. For automatic input, a valid packet must have come in within the last 90 minutes. I know, if it's a weather station connected to your computer it's always coming in, well not quite. I had a case where the cable from the weather station got knocked out and I didn't notice it. A day went by before I realized it and for that entire 24 hours I was transmitting the same temperature as if it was current. By making all weather input to be required to be not less than 90 minutes old, it assures other stations that if they see data from Mac/WinAPRS, it IS current. For those situations where more up-to-date weather data is required, the weather display mode (described below) shows you how old the actual data is.
Barometric Pressure Offset
Some weather units output the ACTUAL barometric pressure, but the pressure reported and understood is the ADJUSTED barometric pressure. The Peet Brothers Weather Station sends the ACTUAL pressure. If you are close to sea level, this can be ignored, but if you live in higher elevations, you will need to set the offset.
The way to figure out this setting is to observe what the Peet Brothers SAYS the pressure is and to listen to the Weather Channel or other weather source and find out what the ACTUAL pressure is.. NOTE: This must be in MILIBARS.
Take the ACTUAL pressure, subtract the REPORTED pressure, multiply by 10, and save that number. The reason for multiplying by 10 is that the value is saved in 10ths for accuracy.
Go to the Weather Settings dialog box under the SETTINGS menu. Find the entry labeled "Press Offset (mb)". Enter the value calculated above into this field.
The Ultimeter II and U-2000 are available from :
The weather station display looks like this:
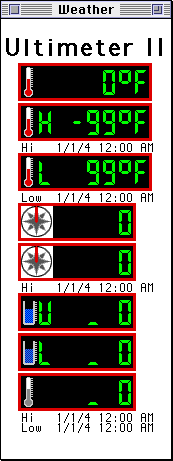
Weather chart
The 24 hour weather chart shows temperature, wind, rain fall etc. for the last 24 hours. This data can be cleared by opening up the weather chart and typing the following:
- "ZT" to zero the temp
- "ZR" to zero the rain
- "ZW" to zero the wind
- "ZP" to zero the pressure
- "ZZ" Refresh the screen, re-calculating the minimums and maximums used for auto-scaling the graphs
National Weather Service Watches and Warnings
APRS has become a very good tool for weather reporting to the National Weather Service,
The NWS office in Mt. Holly, NJ in particular requested the ability to use APRS to help get the word out to Skywarn personnel about activations, watches, and warningspersonnelThese are almost always done on a county-by-county basis.
A feature was added to Mac/WinAPRS to display which counties have Skywarn activation, Watches, or Warnings activated.
There are 2 different options for obtaining the county outlines required for the NWS warnings to work. County Map Files and NWS Shape files
- County Map Files
This is the original method implemented. You must have a folder named COUNTIES and it must contain some special map files. These map files are supplied by us for the ENTIRE United States. Each map file is an outline of exactly one county. For example, NJ_MIDDLESEX.MAP is a map file for the county that I live in, Middlesex County, NJ. You can place files in folders inside of the COUNTIES folder, for example, inside of COUNTIES, I have NJ, MD, and PA folders, inside of them are the county files. This makes it easier to keep track of if you have lots of county files.
The county map files can be found at
ftp://aprs.rutgers.edu/pub/hamradio/APRS/NWSCounties/
Additionally Dale Huguley, kg5qd, has created ZONE files, these can be found at ftp://ftp.gcpoolz.com
- NWS Shape files
This is new as of WinAPRS version 2.5.0 and is now the preferred method. For this method, you create a directory called "NWSshape" and place into it NWS Shape files. There are only 12 files needed and you do not need to use all of them. The files are downloaded directly from NWS web site.
National Weather Services AWIPS Map Database Catalog http://Isl715.nws.noaa.gov/mapdata/newcat/.
The supported files are listed in the order of importance. Each set consists of 3 files, a .dbf which is the DBase file, .shp which is the shape file and .shx which is the index file. All 3 must be present for each database and MUST be the original names.
- County Warning Areas Everyone should have this one. It is the outlines for the County Warning Areas, there are only 121 of these.
- AWIPS Counties These are the county outlines for 3232 counties including Alaska, Hawawii, Peurto Rico, and Guam.
- Zone Forecast Areas These are warning zones, which are similar in size to counties but have different boundaries.
- Coastal and Offshore Marine Zones These are of use mainly to those living near the coast.
IMPORTANT NOTE: By installing all of these files, it can utilize lots of memory.
When there are lots of weather warnings active, screen re-draw time can get much longer.
For that reason, there is now a button on the map window to DISABLE / ENABLE weather warning display.
The default is to display the weather warnings but you can turn it off for any map window.
In the future you will be able to select which county warning areas you want to pay attention to and ignore the rest.
Operation
Mac/WinAPRS can initiate a message sent to NWS-SKYWN, and listing the counties that are activated, any station that has list of counties in the COUNTIES directory will then show that county hi-lighted on the maps.
Yellow means Skywarn activation, orange means Watch and red means Warning.
All activations, warnings and watches have an expiration time on them.
The color hi-lighting of the counties will automatically disappear when that time has passed.
The transmitting station can also deactivate a county which will cancel the current status immediately.
Since the National Weather Service always issues weather bulletins in LOCAL time, these warnings are based on LOCAL time.
It is therefore important that you have your clock set correctly to local time and the UTC offset set to make the ZULU time work properly.
Backwards compatible
Please note that this is NOT a change in the protocol, simply a message addressed to a specific address similar to bulletins.
Older versions and DOS versions will be able to review these messages in the message list
Sending warnings, etc.
The ability to initiate any of these levels of activation is going to be restricted to the NWS office and trained Skywarn personnel, the main reason for this restriction is that the method for sending them out has been made so easy, that we do not want people to do it by accident. If you want the ability to initiate these messages, please contact the authors (Mark Sproul) kb2ici@amsat.org. The intent will be that anyone who is active in Skywarn and therefore a trained Skywarn operator can have this ability to transmit these warnings, but we do not want hundreds of users sending out warning activations by accident or just to see what it does.
IGATE FORWARDING
Stations operating as an IGate can be set up to auto-forward NWS warnings and watches from the internet to local VHF.
A file called COUNTIES.TXT can be placed in the same directory as WinAPRS.EXE, this file contains the county names, one per line exactly as they appear in the NWS county list (i.e. NJ_MIDDLE).
If a NWS warning/watch/etc comes in from TCP/IP address to one of those counties, it is re-transmitted over the LOCAL VHF tnc.
Sample COUNTIES.TXT file
NJ_MERCER
NJ_MIDDLE
NJ_MONMOU
The default is to relay NWS messages from any station, however, if you create a file NWSRELAY.TXT, this file contains the call signs (one per line) of trusted callsgins.
Then an NWS message will ONLY be forwarded if it is from one of those stations.
SSID's are ignored for this process.
Sample NWSRELAY.TXT file
WU2Z
N2NWS
List of APRS contacts for NWS warnings in different areas
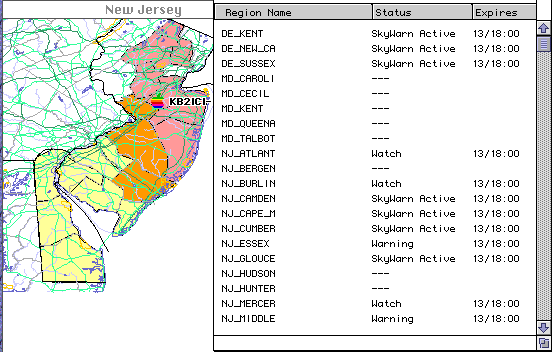
Weather Display Options
You can display weather data along side of the station ICON on the map for all stations that report weather information.
The data format and amount of data displayed can be customized in the Station Display Options dialog box. At present, not all of these features are fully implemented but are displayed here to give you an idea of what's to come.
CALL 1 through CALL 4 are the LOCATIONS you want the CALL SIGN displayed. You can disable the call sign altogether if you like.
Age is the age of the last report. This allows you to keep track on the screen the time of the last report. In the case of severe weather, a report that is 10 minutes old may not be of much use and misleading.
Error is not yet fully defined.
Intellicast Weather Maps
http://www.intellicast.com/ is an excellent weather web site. For example,
http://www.intellicast.com/weather/bgm/radar is the weather radar
for the north east US including Maine to Maryland and as far west as Ohio. These radar images are updated every 30 minutes.
Mac/WinAPRS has the ability to use these images as maps. Additionally, it can retrieve the maps from the web server automatically
and update every 30 minutes automatically. You of course have to be connected to the internet for this to work.
In order to make WinAPRS to understand these images, a .GEO file must be in the IMAGES folder for each region. These
files are included with WinAPRS. The .GEO files are explained under Using Images for Maps.
The 3 letter codes are weather stations abbreviations and many times are also the 3 letter airport code
Global Labels
Global Labels allows you to create a set of map labels that get drawn on ALL maps, these labels are specified by a lat/lon position and a range. If the position is on the map, and the range is correct, the label gets drawn.
Create a folder (directory) called LABELS in the same directory as the application. You can put as many text files containing labels here as you like. These labels will be shown on ALL maps. This allows you to create a list of your own labels that get added to ALL maps. The format for the file is EXACTLY the same as the label entries in a DOS-APRS map file so you can use a text editor to copy any and all labels that you want. There is no limit to the number of labels that you can have in this file (well, it will probably break if you put more than 32,000 labels in it). The label range feature is implemented so that you can set the labels so they won't clutter up the map if you are zoomed out.
The format for the label is Label,latitude,longitude,range
There are 3 different variations of the format
All lines starting with "*" are comment lines and ignored.
In the future you will be able to edit these labels from within MacAPRS / WinAPRS.
Vectors
In the same files as the global labels, you can create global vectors. These would be used to trace the route of a bike race, or to mark of a grid for a special event etc. The vectors are listed in normal Lat/Lon pairs with a "/" in the first column. A "\" in the first column means start a new line (i.e. pick up the pen). Here is a sample
* Trip to South Africa, April, 1997
\40:41:34N,74:10:06W - Newark
/25:47:35N,80:17:25W - Miami
/33:57:53S,18:36:08E - CapeTown
/26:15:00S,28:09:00E - Johanasburg
/29:05:32S,26:18:10E - Bloemfontain
/26:15:00S,28:09:00E - Johanasburg
/16:44:42N,22:57:06W - Isla Dosal
/40:41:34N,74:10:06W - Newark
These vectors will be displayed on all maps at all resolutions, to turn them off, remove them from the labels folder and restart.
It is perfectly OK to mix global labels and vectors in the same file.
This allows you to create a single file for a particular event that you only use once a year.
During the rest of the year, simply move the file to some other directory.
GPS/NMEA data
You can also place raw GPS data streams in the labels folder, they will behave the same as the vectors above. This allows you to drive around a bike race course logging the GPS data, then simply throw that file into the LABELS folder and have an automatic overlay in red of the race course.
Window Config Files
You can save your set of windows including the location of the windows. Win/MacAPRS will automatically load WinAPRS.cfg / MacAPRS.cfg on startup if present. At anytime you can load another config file by simply doing a FILE OPEN. When you do this it will close all existing windows and open up all of the news ones in the specified config file. To save a config file, open up the window(s) (map or list or other) and place them on the screen as desired. Then do a FILE / SAVE WINDOW CONFIG.
GPS Control
Mac/WinAPRS offers the ability to communicate with Garmin GPS units for more than just NMEA data. You can extract waypoints, track logs, even screen shots from most common Garmin GPS units. The ability to extract a track should work with all Garmin GPS units. The ability to extract a screen shot should work with all that support it. Waypoints should work with various models listed below.
In order to use these features, the Garmin GPS unit must be put in Garmin HOST mode, this is normally done under the interface setup section of the GPS.
Waypoint upload/download support for
- GPS 38, GPS 40, GPS 45, GPS 75 and GPS II
- GPS III
- Street Pilot
More will be added along the way, if you have a particular unit you would like supported, just drop me a note and I will add it. There are far to many different waypoint formats to just add them all but I will add all that are requested.
RDF - Radio Direction Finding
Radio Direction Finding, also known as fox hunting, is the use of radio equipment to find the direction of an RF source. With this information obtained from more than one location, triangulation is possible. WinAPRS supports the use of the DF-Jr made by Agrelo Engineering, Agrelo is no longer in buisness, however we still support their unit.
WinAPRS supports two modes of RDF operation, local and remote, these refer to the location of the RDF unit. In local operation, the RDF unit is connected directly to your computer. This can be done from a permanent (non-moving) station or from a mobile station.
Local RDF Operations - stationary
For operations where the RDF unit is connected directly to the computer, every RDF report is directly displayed on the screen. In this mode, the RDF reports are not automatically sent out over the air. The default settings for the DFjr are all that are needed.
Local RDF Operations - mobile
If you are operating an RDF unit from your car while moving, you must have a GPS unit as well. The GPS unit must be configured to output NMEA data (all current models that have data output have NMEA as an option). This data must be feed into the the MPA (Multiple Port Adapter) from Agrelo. The DFjr will then periodically send a GPS string to the computer in addition to the RDF data. This allows you to use both inputs to the computer on a single serial port. This is important since many lap tops only have one port. Additionally, a TNC can be connected to the MPA as well. To enable this feature on the DFjr, use menu option 3, submenu 1. To enable this, press MENU 3 times, make sure sub-menu #1 is selected (the LED at the 11 o'clock position) and press enter.
Remote RDF Operations
In remote operation, the DFjr is listening to one radio and transmitting the direction/strength information out the APRS frequency via a TNC and a SECOND radio. Anyone monitoring this output frequency with APRS will then see the vectors. If you have 2 or more of these units located in different places and both listening to the same frequency. Each time a transmitter is keyed on that frequency, you should get 2 vectors giving you fairly accurate location as to the where the transmitter is.
Set up of a remote DF station is straightforward but requires some complexity.
First there are several parameters in the TNC that have to be set for proper remote RDF operation
- MYCALL RDF1 --- sets the ID of the remote TNC
- BTEXT !1027.19N/06651.91W\ -- this is the string that other APRS stations use to know where the remote unit is located, it must be set correctly for other stations to properly utilize the RDF information sent out by the remote RDF unit. See complete description below.
- BEACON EVERY 30 --- tells the TNC to send its BEACONT TEXT every 300 seconds
- UIMODE ON --- makes the TNC automatically start in CONVERSE mode,
- LFIGNORE ON ---- makes the TNC ignore LF's (line feed characters)
- LOCATION EVERY 0 --- turns of the location text beacon, (beacon text above is used for location information)
- MYALIAS WIDE
The TNC is to be programmed to have a beacon text as follows
BTEXT !hhmm.ddN/hhhmm.ddW\Comment as you like
ddmm.dd
hh = Degrees
mm = minutes
.dd = 100ths of a minute
You set the BEACON RATE with the BEACON EVERY command. This is normally set to something long, for example, a value of 30 will cause it to send out the location every 5 minutes. Most operations should set this to 30 minutes, 180 would be the proper value for 30 minutes.
BE E 30
You program the TNC to automatically come up in CONVERSE mode. Check the TNC manual for this.. Both the Paccomm Picopacket and the Kantronics KPC-3 have this mode. The command for Paccomm is UIMODE ON.
You set the DFjr to only output data when the QUALITY gets above a reasonable number, probably at least 4, but that has to be experimented with..
Then, anytime the TNC receives data from the DFjr, it is of the preset quality and gets transmitted immediately.
Below is an example of data that would be received over the air:
KB2ICI-1>BEACON:!4020.00N/10020.00W\
KB2ICI-1>APRS:%020/5
KB2ICI-1>APRS:%022/6
KB2ICI-1>APRS:%024/5
KB2ICI-2>BEACON:!4040.00N/10040.00W\
KB2ICI-2>APRS:%098/5
KB2ICI-2>APRS:%100/6
KB2ICI-2>APRS:%102/5
NOTE: Each of the different TNCs used must have a different call sign (ID).
Each time data is received from the remote site, the data is displayed on the screen as a colored vector showing the bearing vector.
Mobile operation WITHOUT a computer
A remote station could be setup WITHOUT a computer exactly the same as above with the addition of a GPS input. This is not a very common setup but could be done if another moving DF unit was required and a lap top was not available. The GPS would be connected to the MPA unit and the GPS option in the DFjr (Menu #3) would have to be enabled.
Hints
- The RDF antenna array must be set using TRUE north, not magnetic north.
- Make sure that the DFjr antenna is on a metal surface for proper capacitive grounding.
- Make sure the packet radio antenna is as far away from the DFjr as possible.
Warning / Danger Radius
You can set APRS to notify you if a station moves within a certain distance of your location. This is called WARNING and DANGER radius. To set the radius values, go to SETTINGS / APRS Settings and type in the numbers in the lower left corner (in miles).
To enable a station for warning or danger, go to the station list (or any station list) and select the station. Type D for Danger and W for Warning.
DEM - Digital Elevation Model
DEM files, or Digital Elevation Model files are produced by the USGS. These files are available for all of the US.
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM), consists of a sampled array of elevations for ground positions that are normally at regularly spaced intervals. The 1-Degree DEM (3- by 3-arc-second data spacing) provides coverage in 1- by 1-degree blocks for all of the contiguous United States, Hawaii, and limited portions of Alaska. The basic elevation model is produced by or for the Defense Mapping Agency (DMA), but is distributed by the USGS, EROS Data Center, in the DEM data record format. In reformatting the product the USGS does not change the basic elevation information. 1-degree DEM's are also referred to as "3-arc second" or "1:250,000 scale" DEM data.
These files can be downlodaded from the links below.
You want the 1:250,000-Scale Digital Elevation Model (DEM) version of the files
Please note, UNCOMPRESSED these files are 9 megs each, the compressed version are in GZIP format, the program to uncompress them is:
ftp://prep.ai.mit.edu/pub/gnu/gzip-1.2.4.msdos.exe
I strongly suggest you download the COMPRESSED version and uncompress them, the compression factor is sometimes VERY GOOD
In order to use these files within MacAPRS or WinAPRS, you must create a folder called DEMS and place the UN-COMPRESSED files there. These files are 9 meg EACH when un-compressed. The compressed versions from the USGS FTP site are in GZIP format. This is NOT the same as PKZIP. Programs are available for Mac and Windows to decompress this format.
When you bring up a DEM map, you can overlay any other standard APRS map on TOP of the DEM image. This makes for a very good mapping system with both elevation AND the normal street level data.
You can also have multiple DEMs in a single window, open one as described above, then select another one while holding down the shift key. This will then load it into the same window.
Search and Rescue operations
USER GRIDS
When conducting search and rescue operations, having a locally defined grid can be of tremendous benefit. Mac/WinAPRS allows you to create a local USER GRID for display on your maps.
Note, this has absolutely no effect over the air.
In any map page, there is a button called grids
If you don't have Map buttons, hold down the SHIFT key and do WINDOWS / NEW MAP WINDOW SQUARE
Click on the GRID button, then say NEW GRID, and then click and drag, you will get a square grid with labels.
Again, this is for local display ONLY and NOTHING is transmitted for this feature. It allows a command post to refer to grids while conducting a search.
DX Cluster Support
Mac/WinAPRS supports DX Cluster data in a different light than normal DX cluster operation.
First it operates in non-connected mode watching ALL of the traffic from the DX Cluster so you are not WAITING for your turn in the queue.
Second, it displays the contacts on the map and helps with antenna bearing.
To use the DX Cluster option of WinAPRS/MacAPRS you need to do the following:
- Make sure the file DXlist.dat is in the DATA subdirectory
- Once you have done this, you can verify it by bringing up the DXCC LIST (from the LIST menu). This should show you the list of Call-sign prefixes and their locaitons. Double clicking on one of these stations will show you where that country is (If a map that has it is currently open)
- Go to the POSITION REPORT RATE settings dialog box and set all of the VHF transmit rates to ZERO. This is because you do not want to transmit APRS data on the DX Cluster frequency.
- Turn your radio to the DX CLUSTER frequency and let it run.
You should get icons showing 'radio towers' for each DX spot that you
receive.
Space Mode
Space Mode exists solely for the purpose of MIR testing. To use space mode you MUST do these things IN ORDER
- Make sure your Lat/Lon are set if not already
- Enable Space Mode under the Master Mode Menu (under SETTINGS)
- Open VHF TNC
Space mode uses your GRID SQUARE for your to field (Unproto destination field), this gets set automatically when you open the TNC but SPACE mode must be set first. For the grid square to be set correctly, you must have your Lat/Lon set.
When in Space Mode, the position report and the proto path are considerably different then normal, these follow Bob Bruniga's definition for the testing.
APRS uses
- APRS and the National Weather Services
All of the versions of APRS are being used quite successfully in conjunction with NWS activities. Several NWS locations have APRS stations set up to monitor real-time weather reports from other APRS stations in the area.
There are many features built into MacAPRS/WinAPRS to enhance this mode of operation. You can set the display mode to show ONLY weather stations. This will allow you to monitor on the map, the temperature, rainfall, wind, etc. at various locations without all of the rest of the stations being visible. See the section on Weather Display Options
- Search and Rescue
Several features have been added specifically to enhance the usefulness for Search and Rescue operations. The first of these is CAP/SAR grids. The grid locator system used by the Civil Air Patrol. This grid overlay can be drawn on any map at any time by selecting the CAP GRIDS command from the DISPLAY menu or by typing "C" for any map. You can also turn this on permanently in the MAP DISPLAY OPTIONS. It can be set for just the one map, for all maps and for the default configuration of maps.
The CAP/SAR grid is a two level grid, the first level is associated with air space control, the next level is a numbered sequence. Mac/WinAPRS automatically chooses the appropriate level of grid display depending on your map scale.
- Fox hunting
MacAPRS/WinAPRS works with the Agrello DFjr Radio Direction Finding unit. This can be setup to work for fox hunting applications
- (I will be expanding this section as I have time)
Known limitations
As with any software package there are limitations. This is a list of specific issues that you may encounter.

- Station Icons under Windows 3.1 - As any of the beta testers remember, there were lots of problems with the size of the station Icons. This has been fixed but the fix is not supported under Win32s (Windows 3.1), therefore when running 3.1, the station icons show up as red, blue, or black circles. The alternative is LARGE icons which looks much worse. I will be working on a better implementation for future versions. You can enable the large Icons by turning "Station Icons" on in the display menu. But be warned, they are VERY large on the map.

- The Mac version does not support HSP and is not likly to. Use instead a TNC such as the Pico-Packet with a built-in GPS input.
SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE
MacAPRS and WinAPRS are written in C and C++. They do NOT use the Microsoft Foundation Class (MFC) or any other C++ framework. They are written using a framework that I wrote for cross platform software. This architecture started out as normal C as far back as 1990 and in February of 1997 started migrating to C++. Much of the code is still written in C and much of it is in C++.
MacAPRS and WinAPRS are ONE set of source code written to work on both platforms and eventually X-Windows (Linux). The only part of the code that is not the same is the serial I/O drivers and the main event loop. ALL remaining portions of the code are one unified set of source code.
MacAPRS and WinAPRS are both written and compiled using CodeWarrior from Metrowerks. CodeWarrior is a full featured development environment that is available for both Mac and Windows. It allows compiling for Mac AND Windows on either platform. It does NOT convert software to run on another platform, just acts as a cross-compiler/debugger.
Serial Port problems
During the beta testing of WinAPRS, the most common problem had to do with serial ports. This seems to be a standard problem on PCs. I have done everything I can to write to the proper Windows guidelines to make the serial ports work as cleanly as possible. If you are having problems, try this.
When the start-up dialog box is displayed, hold the SHIFT key down while clicking the OK button. This will turn on serial port debugging messages. This may help in solving serial port problems.
Troubleshooting
Here are some hints for common problems.
- If you are running Windows 3.1/3.11 and when you try to run the application and it IMMEDIATELY quits, then you do NOT have Win32S installed. Win32S MUST be installed FIRST!!!!
- Maps don't show up. All maps MUST be in a folder (directory) called "Maps". This folder must be in the same folder as the application itself.
- You have the Maps folder but WinAPRS does not find it. If you have created a icon shortcut that is somewhere else, you must select the properties and make sure that the application folder is set under advanced settings.
- New maps placed in the Maps folder will NOT show up until the next time you start the program.
- Serial port opens but no stations show up If you use other programs with your tnc, the tnc may be left in HOST mode, both AEA/TimeWave and Kantronics TNCs have a HOST mode. Under SETTINGS / TNC-COMMANDS, there are options for VHF and HF to exit each of these modes. For example if you had an AEA PK-232 set up for VHF you would do VHF-EXIT AEA HOST MODE. This must be done AFTER the port has been opened.
- Communications problems for Windows. Serial port issues can be a large problem for Windows users. Every effort has been made to exactly follow the MS-Windows programming guidelines for dealing with serial ports. The software goes through the operating system to access the ports. There is no knowledge of the address or IRQs in the program. We have done testing with up to 8 ports in a machine and all has worked well. All problems that we have run into have been traced to some com port setting or IRQ conflict.
- If your settings get messed up and you cannot get them to set correctly, delete the preferences file. On the Mac this is the "MacAPRS.prefs" file in the "Preferences" folder in the system folder. For Windows, it is the WinAPRS.prf in the same folder as the application. Note, if you do this you will have to re-enter ALL of your settings including your validation number.
- Serial I/O doesn't work and DLL failed to load message appears. The DLLs are missing, see the installation section.
- Serial I/O doesn't work: When the start-up dialog box is displayed, hold the SHIFT key down while clicking the OK button. This will turn on serial port debugging messages. This may help in solving serial port problems.
- Callbook CD-ROM database is not working: If you are using the SAMS or QRZ CD-ROM, you need to create a database index file. This can be done from the CALLBOOK setup dialog box.
- If you are having problems with HSP mode, do the following:
- Verify that HSP and Allow GPS are both checked for the port being used in the SERIAL PORT dialog box.
- Open the port
- Open the terminal window (under Windows Menu)
- Connect the GPS to the connector that the TNC is normally connected. This will verify that the GPS data is properly coming through the cable. If GPS data is not coming in, then the GPS is not cabled correctly or it is not set correctly for continuous output.
- Once the above is working, connect the GPS back to the GPS side and leave the TNC cable disconnected. Watch the terminal window again for at least a few minutes, from 56 seconds past the minute to 0 past the minute, GPS data should appear on the screen.
- Help window doesn't contain any information: Make sure you have a "DOCS" directory in the same directory as WinAPRS.exe and make sure that WAPRSdoc.htm is in that directory.
- If stations appear on your station list but not on your map. Make sure that HEADERLN is OFF and if you are running an AEA TNC, make sure that BBSMSGS is on. Note, only some AEA tncs have this command so if yours does not, don't worry about it.
Other APRS Information on the web
Related information
INDEX
NOTE: All manuals should have indexes, using the Web for documentation makes indexes much harder. Please note that this index is intended for the PRINTED version may often be off by a page or more. I realize that this may be a minor inconvenience, but I think it is better than no index at all.
This index was setup with the document printed by Netscape with the following settings.
FONTS
Proportional Times size =12
Fixed Courier Size = 10
Page Setup
both header (title) and footer (page numbers) are turned on
- 3rd Party Message Forwarding . . .
- Airports . . .22-23
- Alarm sounds . . .27
- Alternate Paths. . .34
- Announcements . . .25
- APRS Objects . . .26
- Audio Alarms . . .27
- Auto-refresh maps . . .24
- Bulletins . . .25
- CD-ROM Database . . .31
- Civil Air Patrol . . .25,49
- Configuration . . .11-13--
- Danger Radius . . .
- DEM files . . .
- Diagnostics . . .8
- Digipeaters . . .22
- Display Menu . . .16
- DLL (Dynamic Link Library) . . .7,8,29
- Edit Menu . . .15
- Elevation . . .
- FCC Database . . .31
- File Menu . . .15
- Fox hunting . . .28
- Frequencies . . .12
- GATE . . .21
- Gateway operation . . .28
- Global Labels . . .33-34
- Grid Square . . .16
- GPS . . .
- Help Window . . .14
- HSP Support . . .21
- IGate operation . . .
- INIT***.TNC . . .10
- Installation . . .10
- Keyboard short cuts . . .22-23
- List Windows . . .16
- Logging . . .18
- Logging Menu . . .19
- MapBlast map server . . .
- Maps . . .14
- Map Display Options . . .24
- Map list . . .13
- Map Menu . . .15
- Master Mode . . .9
- Menu commands . . .18-20
- Messages . . .20
- Mouse down short cuts . . .22
- National Weather Service . . .30
- NMEA . . .
- Objects . . .20-21
- Other Information . . .30
- Overlay Files . . .28
- Printing . . .24
- RDF (Radio Directon Finding) . . .35
- RELAY . . .21
- RESTORE.TNC . . .10
- Search and Rescue . . .16
- Serial Port problems . . .29
- Selective query . . .18
- Settings Menu . . .15
- Shareware fees . . .4
- Skywarn . . .30
- Sounds . . .21
- System requirements . . .9
- TCP/IP. . .28
- Terminal window . . .20
- Tiger map server . . .
- TNC commands . . .13
- TNC Settings . . .10
- Troubleshooting . . .29
- Unproto path . . .25-27
- USGS . . .12
- Version numbers . . .4
- Warning Radius . . .
- Web based map servers . . .
- Wave files, .WAV . . .21-22
- Weather . . .28
- Weather Display Options . . .32
- Weather Input . . .29
- WIDE . . .21
- Win32S . . .9
- Window config files . . .35
- Windows 3.1 . . .10-11
- Windows 95 . . .7
- Windows NT . . .7
- Winds Aloft . . .33
- Zipcodes . . .16,28
Back to APRS home page
This documentation is © 1996-97 by Mark and Keith Sproul.
APRS™ © Bob Bruninga (WB4APR)
MacAPRS™, WinAPRS™ © by Mark Sproul (KB2ICI) and Keith Sproul (WU2Z).
Access counter





 Mac Version
Mac Version
 Windows Version
Windows Version
 System Requirements for Macintosh
System Requirements for Macintosh System Requirements for Windows
System Requirements for Windows WinAPRS is normally distributed via the internet as a ZIP file,
To unzip the file
WinAPRS is normally distributed via the internet as a ZIP file,
To unzip the file




 Originally I thought that the settings for WinAPRS would have to be dramatically different from what was done for MacAPRS, this is due to the vastly different implementation of dialogs for Windows versus the MacOS. I was able to write software that read the Mac dialog resources and output Windows dialog resource descriptions. This made the conversion dramatically easier and made the dialog boxes for both versions practically identical.
Originally I thought that the settings for WinAPRS would have to be dramatically different from what was done for MacAPRS, this is due to the vastly different implementation of dialogs for Windows versus the MacOS. I was able to write software that read the Mac dialog resources and output Windows dialog resource descriptions. This made the conversion dramatically easier and made the dialog boxes for both versions practically identical.
 Serial Port - Set up comm port parameters
Serial Port - Set up comm port parameters
 Communications - Set up comm ports for input. This is a sub menu.
Communications - Set up comm ports for input. This is a sub menu.
 Enable Sound - Enable / Disable audio alarms
Enable Sound - Enable / Disable audio alarms
 Sound settings - set the voices for text-to-speech.
Sound settings - set the voices for text-to-speech.
 Balloon settings - Used for calculating information when tracking balloons.
Balloon settings - Used for calculating information when tracking balloons.
 GPS settings - Setting special things for GPS input
GPS settings - Setting special things for GPS input


 The map file format for WinAPRS is EXACTLY the same as MacAPRS.
This means that all of the maps developed for MacAPRS are usable for WinAPRS.
You must have a "Maps" folder (directory) in the same folder as the MacAPRS / WinAPRS application.
All Maps must be placed inside this folder.
You can have folders inside of the map folder.
These will be displayed as hierarchical menus.
The map file format for WinAPRS is EXACTLY the same as MacAPRS.
This means that all of the maps developed for MacAPRS are usable for WinAPRS.
You must have a "Maps" folder (directory) in the same folder as the MacAPRS / WinAPRS application.
All Maps must be placed inside this folder.
You can have folders inside of the map folder.
These will be displayed as hierarchical menus.
 Some of the maps for Macintosh on the TAPR FTP site are in Macintosh "sit.hqx" format.
This is similar to ZIP format for PCs, but of course not compatible.
We have found a PC program called SITEX10.EXE that allows decompression of these files on PCs.
It can be found at:
Some of the maps for Macintosh on the TAPR FTP site are in Macintosh "sit.hqx" format.
This is similar to ZIP format for PCs, but of course not compatible.
We have found a PC program called SITEX10.EXE that allows decompression of these files on PCs.
It can be found at:







 There are many different types of list windows in MacAPRS / WinAPRS. Each of the windows supplies a list of information organized in a different manner. Some of the information is constant such as the current list of maps. Most of the information is dynamic and will change as stations appear, etc.
There are many different types of list windows in MacAPRS / WinAPRS. Each of the windows supplies a list of information organized in a different manner. Some of the information is constant such as the current list of maps. Most of the information is dynamic and will change as stations appear, etc.
 Under the "Windows" menu, select the terminal window command. This will bring up a terminal window that will allow you to talk directly to your TNC or other port. It will connect to whichever port you have open. If you do not have any port open, it will not let you open the terminal window. During the time that the terminal window is open, APRS data STILL gets processed. If the Terminal Window is the FRONT MOST WINDOW, then WinAPRS will NOT output any commands or strings to the TNC. If the terminal window is not the currently active window, then WinAPRS will output as normal. At ALL times, the INPUT from the port is still processed normally by WinAPRS so you do not lose any data.
Under the "Windows" menu, select the terminal window command. This will bring up a terminal window that will allow you to talk directly to your TNC or other port. It will connect to whichever port you have open. If you do not have any port open, it will not let you open the terminal window. During the time that the terminal window is open, APRS data STILL gets processed. If the Terminal Window is the FRONT MOST WINDOW, then WinAPRS will NOT output any commands or strings to the TNC. If the terminal window is not the currently active window, then WinAPRS will output as normal. At ALL times, the INPUT from the port is still processed normally by WinAPRS so you do not lose any data.
 On the Mac you can print any and all windows. The print command applies to the current window. The map windows will be resized to fit the paper of the currently selected printer so they should never take up more than one page on the output. Also the print code has been written so that it works well with pen plotters and will take proper advantage of the large print area of a large pen plotter.
On the Mac you can print any and all windows. The print command applies to the current window. The map windows will be resized to fit the paper of the currently selected printer so they should never take up more than one page on the output. Also the print code has been written so that it works well with pen plotters and will take proper advantage of the large print area of a large pen plotter.
 WinAPRS can print the list windows, map windows do not print at this time.
WinAPRS can print the list windows, map windows do not print at this time.

 MacAPRS and WinAPRS support several weather stations. Currently supported units are:
MacAPRS and WinAPRS support several weather stations. Currently supported units are:




